Robust, high-throughput solution structural analyses by small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
- PMID: 19620974
- PMCID: PMC3094553
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1353
Robust, high-throughput solution structural analyses by small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
Abstract
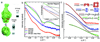
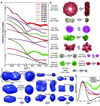
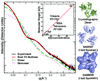
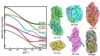
We present an efficient pipeline enabling high-throughput analysis of protein structure in solution with small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Our SAXS pipeline combines automated sample handling of microliter volumes, temperature and anaerobic control, rapid data collection and data analysis, and couples structural analysis with automated archiving. We subjected 50 representative proteins, mostly from Pyrococcus furiosus, to this pipeline and found that 30 were multimeric structures in solution. SAXS analysis allowed us to distinguish aggregated and unfolded proteins, define global structural parameters and oligomeric states for most samples, identify shapes and similar structures for 25 unknown structures, and determine envelopes for 41 proteins. We believe that high-throughput SAXS is an enabling technology that may change the way that structural genomics research is done.
Figures

References
-
- Robinson CV, Sali A, Baumeister W. The molecular sociology of the cell. Nature. 2007;450:973. - PubMed
-
- Green BD, Keller M. Capturing the uncultivated majority. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006;17:236. - PubMed
-
- Wilmes P, Bond PL. Metaproteomics: studying functional gene expression in microbial ecosystems. Trends Microbiol. 2006;14:92. - PubMed
-
- Putnam CD, Hammel M, Hura GL, Tainer JA. X-ray solution scattering (SAXS) combined with crystallography and computation: defining accurate macromolecular structures, conformations and assemblies in solution. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2007;40:191. - PubMed
-
- Fox BG, et al. Structural genomics: from genes to structures with valuable materials and many questions in between. Nat. Methods. 2008;5:129. - PubMed

