InvAluable junk: the cellular impact and function of Alu and B2 RNAs
- PMID: 19621349
- PMCID: PMC4049031
- DOI: 10.1002/iub.227
InvAluable junk: the cellular impact and function of Alu and B2 RNAs
Abstract
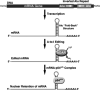
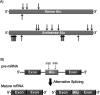
The short interspersed elements (SINEs) Alu and B2 are retrotransposons that litter the human and mouse genomes, respectively. Given their abundance, the manner in which these elements impact the host genome and what their biological functions might be is of significant interest. Finding that Alu and B2 SINEs are transcribed, both as distinct RNA polymerase III transcripts and as part of RNA polymerase II transcripts, and that these SINE encoded RNAs indeed have biological functions has refuted the historical notion that SINEs are merely "junk DNA." This article reviews currently known cellular functions of both RNA polymerase II and RNA polymerase III transcribed Alu and B2 RNAs. These RNAs, in different forms, control gene expression by participating in processes as diverse as mRNA transcriptional control, A-to-I editing, nuclear retention, and alternative splicing. Future studies will likely reveal additional contributions of Alu and B2 RNAs as regulators of gene expression.
Figures
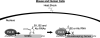
References
-
- Cordaux R, Hedges DJ, Herke SW, Batzer MA. Estimating the retrotransposition rate of human Alu elements. Gene. 2006;373:134–137. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Waterston RH, Lindblad-Toh K, Birney E, Rogers J, Abril JF, Agarwal P, Agarwala R, Ainscough R, Alexandersson M, An P, et al. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420:520–562. - PubMed
-
- Jurka J, Kapitonov VV, Kohany O, Jurka MV. Repetitive sequences in complex genomes: structure and evolution. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2007;8:241–259. - PubMed
-
- Dewannieux M, Heidmann T. L1-mediated retrotransposition of murine B1 and B2 SINEs recapitulated in cultured cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;349:241–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

