Discovery of dermorphin-based affinity labels with subnanomolar affinity for mu opioid receptors
- PMID: 19621878
- PMCID: PMC2788677
- DOI: 10.1021/jm9007592
Discovery of dermorphin-based affinity labels with subnanomolar affinity for mu opioid receptors
Abstract
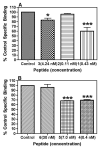
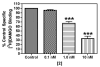
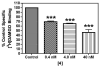
A series of potent electrophilic affinity labels (IC(50) = 0.1-5 nM) containing either a bromoacetamide or isothiocyanate based on the mu opioid receptor (MOR) selective peptide dermorphin were prepared. All four analogues exhibited wash resistant inhibition of [(3)H]DAMGO binding at subnanomolar to nanomolar concentrations, suggesting that these analogues bind covalently to MOR. To our knowledge, these peptides are the highest affinity peptide-based affinity labels for MOR reported to date.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dermorphin-based potential affinity labels for mu-opioid receptors.J Pept Res. 2003 Jan;61(1):40-5. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3011.2003.20030.x. J Pept Res. 2003. PMID: 12472847
-
Synthesis and evaluation of N,N-dialkyl enkephalin-based affinity labels for delta opioid receptors.J Med Chem. 2000 Oct 19;43(21):3941-8. doi: 10.1021/jm000123u. J Med Chem. 2000. PMID: 11052799
-
Synthesis and evaluation of potential affinity labels derived from endomorphin-2.J Pept Res. 2003 Feb;61(2):58-62. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3011.2003.00029.x. J Pept Res. 2003. PMID: 12492899
-
Structure-activity relationships of dermorphin analogues containing N-substituted amino acids in the 2-position of the peptide sequence.Int J Pept Protein Res. 1995 Jul;46(1):47-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1995.tb00580.x. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1995. PMID: 7558596
-
Dermorphin tetrapeptide analogs as potent and long-lasting analgesics with pharmacological profiles distinct from morphine.Peptides. 2011 Feb;32(2):421-7. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.11.013. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Peptides. 2011. PMID: 21126548 Review.
Cited by
-
Solution-phase-peptide synthesis via the group-assisted purification (GAP) chemistry without using chromatography and recrystallization.Chem Commun (Camb). 2014 Feb 7;50(10):1259-61. doi: 10.1039/c3cc48509a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2014. PMID: 24336500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldrich JV, Vigil-Cruz SC. Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery. 6th ed Vol. 6. John Wiley, Inc; New York: 2003. Narcotic Analgesics; pp. 329–481.
-
- Chen Y, Mestek A, Liu J, Hurley JA, Yu L. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a mu-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993;44:8–12. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda K, Kato S, Mori K, Nishi M, Takeshima H. Primary structures and expression from cDNAs of rat opioid receptor delta- and mu-subtypes. FEBS Lett. 1993;327:311–314. - PubMed
-
- Law PY, Wong YH, Loh HH. Mutational analysis of the structure and function of opioid receptors. Biopolymers (Pept. Sci.) 1999;51:440–455. - PubMed
-
- Takemori AE, Portoghese PS. Affinity labels for opioid receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1985;25:193–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

