An intracellular trafficking pathway in the seminiferous epithelium regulating spermatogenesis: a biochemical and molecular perspective
- PMID: 19622063
- PMCID: PMC2758293
- DOI: 10.1080/10409230903061207
An intracellular trafficking pathway in the seminiferous epithelium regulating spermatogenesis: a biochemical and molecular perspective
Abstract
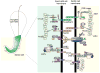
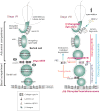
During spermatogenesis in adult rat testes, fully developed spermatids (i.e. spermatozoa) at the luminal edge of the seminiferous epithelium undergo "spermiation" at stage VIII of the seminiferous epithelial cycle. This is manifested by the disruption of the apical ectoplasmic specialization (apical ES) so that spermatozoa can enter the tubule lumen and to complete their maturation in the epididymis. At the same time, the blood-testis barrier (BTB) located near the basement membrane undergoes extensive restructuring to allow transit of preleptotene spermatocytes so that post-meiotic germ cells complete their development behind the BTB. While spermiation and BTB restructuring take place concurrently at opposite ends of the Sertoli cell epithelium, the biochemical mechanism(s) by which they are coordinated were not known until recently. Studies have shown that fragments of laminin chains are generated from the laminin/integrin protein complex at the apical ES via the action of MMP-2 (matrix metalloprotease-2) at spermiation. These peptides serve as the local autocrine factors to destabilize the BTB. These laminin peptides also exert their effects on hemidesmosome which, in turn, further potentiates BTB restructuring. Thus, a novel apical ES-BTB-hemidesmosome regulatory loop is operating in the seminiferous epithelium to coordinate these two crucial cellular events of spermatogenesis. This functional loop is further assisted by the Par3/Par6-based polarity protein complex in coordination with cytokines and testosterone at the BTB. Herein, we provide a critical review based on the latest findings in the field regarding the regulation of these cellular events. These recent findings also open up a new window for investigators studying blood-tissue barriers.
Figures



References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Science; 2002.
-
- Aumailley M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Carter W, Deutzmann R, Edgar D, Ekblom P, Engel J, Engvall E, Hohenester E, Jones J, et al. A simplified laminin nomenclature. Matrix Biol. 2005;24:326–332. - PubMed
-
- Bart J, Hollema H, Groen HJ, de Vries EG, Hendrikse NH, Sleijfer DT, Wegman TD, Vaalburg W, van der Graaf WT. The distribution of drug-efflux pumps, P-gp, BCRP, MRP1 and MRP2, in the normal blood-testis barrier and in primary testicular tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:2064–2070. - PubMed
-
- Bernacki J, Dobrowolska A, Nierwinska K, Malecki A. Physiology and pharmacological role of the blood-brain barrier. Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60:600–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
