Prostaglandin E2, Wnt, and BMP in gastric tumor mouse models
- PMID: 19622104
- PMCID: PMC11159255
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01258.x
Prostaglandin E2, Wnt, and BMP in gastric tumor mouse models
Abstract
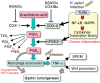
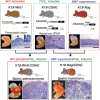
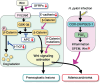
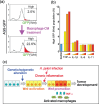
The development of gastric cancer is closely associated with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. The expression of cylooxigenase-2 (COX-2), a rate-limiting enzyme for prostaglandin biosynthesis, is induced in H. pylori-associated chronic gastritis, which thus results in the induction of proinflammatory prostaglandin, PGE(2). The COX-2/PGE(2) pathway plays a key role in gastric tumorigenesis. On the other hand, several oncogenic pathways have been shown to trigger gastric tumorigenesis. The activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is found in 30-50% of gastric cancers, thus suggesting that Wnt signaling plays a causal role in gastric cancer development. Mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway are responsible for the subset of juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) that develops hamartomas in the gastrointestinal tract. BMP suppression appears to contribute to gastric cancer development because gastric cancer risk is increased in JPS. Wnt signaling is important for the maintenance of gastrointestinal stem cells, while BMP promotes epithelial cell differentiation. Accordingly, it is possible that both Wnt activation and BMP suppression can cause gastric tumorigenesis through enhancement of the undifferentiated status of epithelial cells. Recent mouse model studies have indicated that induction of the PGE(2) pathway is required for the development of both gastric adenocarcinoma and hamartoma in the Wnt-activated and BMP-suppressed gastric mucosa, respectively. This article reviews the involvement of the PGE(2), Wnt, and BMP pathways in the development of gastric cancer, and gastric phenotypes that are found in transgenic mouse models of PGE(2) induction, Wnt activation, BMP suppression, or a combination of these pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mouse models of gastric tumors: Wnt activation and PGE2 induction.Pathol Int. 2010 Sep;60(9):599-607. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02567.x. Pathol Int. 2010. PMID: 20712645 Review.
-
Induction of prostaglandin E2 pathway promotes gastric hamartoma development with suppression of bone morphogenetic protein signaling.Cancer Res. 2009 Apr 1;69(7):2729-33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4394. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19318548
-
Carcinogenesis in mouse stomach by simultaneous activation of the Wnt signaling and prostaglandin E2 pathway.Gastroenterology. 2006 Oct;131(4):1086-95. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.07.014. Gastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 17030179
-
Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by the prostaglandin E(2) receptor EP4 pathway during gastric tumorigenesis.Cancer Sci. 2011 Apr;102(4):713-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01847.x. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21205091 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of stem cell signaling network due to germline mutation, SNP, Helicobacter pylori infection, epigenetic change and genetic alteration in gastric cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2007 Jun;6(6):832-9. doi: 10.4161/cbt.6.6.4196. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17568183 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells.Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(2):184-92. doi: 10.7150/ijms.3859. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Int J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22359486 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO3 is a latent tumor suppressor for FOXO3-positive and cytoplasmic-type gastric cancer cells.Oncogene. 2021 Apr;40(17):3072-3086. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01757-x. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33795838 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenetic mechanisms in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 14;20(38):13804-19. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13804. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25320518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variant of cyclooxygenase-2 in gastric cancer: More inflammation and susceptibility.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jul 28;27(28):4653-4666. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4653. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34366627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression analysis of a Helicobacter pylori-infected and high-salt diet-treated mouse gastric tumor model: identification of CD177 as a novel prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul 30;13:122. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-13-122. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23899160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thun MJ, Namboodiri MM, Heath CW Jr. Aspirin use and reduced risk of fatal colon cancer. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 1593–6. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher BS, Kujubu DA, Perrin DM, Herschman HR. Structure of the mitogen‐inducible TIS10 gene and demonstration that the TIS10‐encoded protein is a functional prostaglandin G/H synthase. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 4338–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

