c-MycERTAM transgene silencing in a genetically modified human neural stem cell line implanted into MCAo rodent brain
- PMID: 19622162
- PMCID: PMC2725042
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-10-86
c-MycERTAM transgene silencing in a genetically modified human neural stem cell line implanted into MCAo rodent brain
Abstract
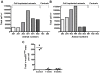
Background: The human neural stem cell line CTX0E03 was developed for the cell based treatment of chronic stroke disability. Derived from fetal cortical brain tissue, CTX0E03 is a clonal cell line that contains a single copy of the c-mycERTAM transgene delivered by retroviral infection. Under the conditional regulation by 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT), c-mycERTAM enabled large-scale stable banking of the CTX0E03 cells. In this study, we investigated the fate of this transgene following growth arrest (EGF, bFGF and 4-OHT withdrawal) in vitro and following intracerebral implantation into a mid-cerebral artery occluded (MCAo) rat brain. In vitro, 4-weeks after removing growth factors and 4-OHT from the culture medium, c-mycERTAM transgene transcription is reduced by ~75%. Furthermore, immunocytochemistry and western blotting demonstrated a concurrent decrease in the c-MycERTAM protein. To examine the transcription of the transgene in vivo, CTX0E03 cells (450,000) were implanted 4-weeks post MCAo lesion and analysed for human cell survival and c-mycERTAM transcription by qPCR and qRT-PCR, respectively.
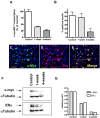
Results: The results show that CTX0E03 cells were present in all grafted animal brains ranging from 6.3% to 39.8% of the total cells injected. Prior to implantation, the CTX0E03 cell suspension contained 215.7 (SEM = 13.2) copies of the c-mycERTAM transcript per cell. After implantation the c-mycERTAM transcript copy number per CTX0E03 cell had reduced to 6.9 (SEM = 3.4) at 1-week and 7.7 (SEM = 2.5) at 4-weeks. Bisulfite genomic DNA sequencing of the in vivo samples confirmed c-mycERTAM silencing occurred through methylation of the transgene promoter sequence.
Conclusion: In conclusion the results confirm that CTX0E03 cells downregulated c-mycERTAM transgene expression both in vitro following EGF, bFGF and 4-OHT withdrawal and in vivo following implantation in MCAo rat brain. The silencing of the c-mycERTAM transgene in vivo provides an additional safety feature of CTX0E03 cells for potential clinical application.
Figures


References
-
- Sinden JD, Rashid-Doubell F, Kershaw TR, Nelson A, Chadwick A, Jat PS, Noble MD, Hodges H, Gray JA. Recovery of spatial learning by grafts of a conditionally immortalized hippocampal neuroepithelial cell line into the ischaemia-lesioned hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1997;81:599–608. doi: 10.1016/S0306-4522(97)00330-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Veizovic T, Beech JS, Stroemer RP, Watson WP, Hodges H. Resolution of stroke deficits following contralateral grafts of conditionally immortal neuroepithelial stem cells. Stroke. 2001;32:1012–1019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

