Pineal function: impact of microarray analysis
- PMID: 19622385
- PMCID: PMC3138125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.07.010
Pineal function: impact of microarray analysis
Abstract
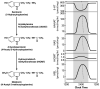
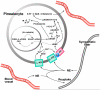
Microarray analysis has provided a new understanding of pineal function by identifying genes that are highly expressed in this tissue relative to other tissues and also by identifying over 600 genes that are expressed on a 24-h schedule. This effort has highlighted surprising similarity to the retina and has provided reason to explore new avenues of study including intracellular signaling, signal transduction, transcriptional cascades, thyroid/retinoic acid hormone signaling, metal biology, RNA splicing, and the role the pineal gland plays in the immune/inflammation response. The new foundation that microarray analysis has provided will broadly support future research on pineal function.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- AITKEN A. 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:162–72. - PubMed
-
- AUERBACH DA, KLEIN DC, KIRK KL, CANTACUZENE D, CREVELING CR. Effects on fluorine analogs of norepinephrine on stimulation of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and binding to beta-adrenergic receptors in intact pinealocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981a;30:1085–9. - PubMed
-
- AUERBACH DA, KLEIN DC, WOODARD C, AURBACH GD. Neonatal rat pinealocytes: typical and atypical characteristics of [125I]iodohydroxybenzylpindolol binding and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate accumulation. Endocrinology. 1981b;108:559–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

