The Role of Th17 in Neuroimmune Disorders: Target for CAM Therapy. Part I
- PMID: 19622600
- PMCID: PMC3139523
- DOI: 10.1093/ecam/nep062
The Role of Th17 in Neuroimmune Disorders: Target for CAM Therapy. Part I
Abstract
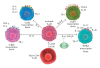
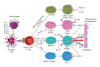
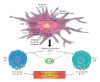
CD4(+) effector cells, based on cytokine production, nuclear receptors and signaling pathways, have been categorized into four subsets. T-helper-1 cells produce IFN-γ, TNF-β, lymphotoxin and IL-10; T-helper-2 cells produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13, IL-21 and IL-31; T-helper-3, or regulatory T-cells, produce IL-10, TGF-β and IL-35; and the recently discovered T-helper-17 cell produces IL-17, IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-21, IL-26 and CCL20. By producing IL-17 and other signaling molecules, Th17 contributes to the pathogenesis of multiple autoimmune diseases including allergic inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune gastritis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. In this article, we review the differential regulation of inflammation in different tissues with a major emphasis on enhancement of neuroinflammation by local production of IL-17 in the brain. By understanding the role of pathogenic factors in the induction of autoimmune diseases by Th17 cells, CAM practitioners will be able to design CAM therapies targeting Th17 and associated cytokine activities and signaling pathways to repair the intestinal and blood-brain barriers for their patients with autoimmunities, in particular, those with neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.
Figures
References
-
- Coffman RL, Carty JA. T cell activity that enhances polyclonal IgE production and its inhibition by interferon-gamma. Journal of Immunology. 1986;136:949–954. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. Journal of Immunology. 1986;136(7):2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Coffman RL. Origins of the TH1-TH2 model: a personal perspective. Nature Immunology. 2006;7(6):539–541. - PubMed
-
- Wilson CB, Rowell E, Sekimata M. Epigenetic control of T-helper-cell differentiation. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2009;9(2):91–105. - PubMed
-
- Moss RB, Moll T, El-Kalay M, et al. Th1/Th2 cells in inflammatory disease states: therapeutic implications. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 2004;4(12):1887–1896. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

