Nocardia iowensis sp. nov., an organism rich in biocatalytically important enzymes and nitric oxide synthase
- PMID: 19622667
- PMCID: PMC2759412
- DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.007427-0
Nocardia iowensis sp. nov., an organism rich in biocatalytically important enzymes and nitric oxide synthase
Abstract
Nocardia strain NRRL 5646, isolated from a garden soil sample in Osceola, Iowa, USA, was initially of interest as an antibiotic producer. It contained biocatalytically important enzymes and represented the first described nitric oxide synthase enzyme system in bacteria. The present polyphasic taxonomic study was undertaken to differentiate strain NRRL 5646(T) from related species of the genus Nocardia. Chemotaxonomic analyses included determinations of the fatty acid methyl ester profile (C(16 : 1)omega6c/C(16 : 1)omega7c, C(16 : 0), C(18 : 1)omega9c and C(18 : 0) 10-methyl as major components), quinone [cyclo MK-8(H(4)) as the major component], polar lipid (diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylinositol mannoside as major components) and mycolic acid. These results supported its placement within the genus Nocardia. Biochemical testing and 16S rRNA, 65-kDa heat-shock protein (hsp65) and preprotein translocase (secA1) gene sequence analyses differentiated strain NRRL 5646(T) from recognized Nocardia species. Previous studies have demonstrated that other genetic sequences (carboxylic acid reductase, Nocardia phosphopantetheinyl transferase and GTP cyclohydrolase I) from strain NRRL 5646(T) can also be used to substantiate its uniqueness. The level of 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity between strain NRRL 5646(T) and the type strains of Nocardia tenerifensis and Nocardia brasiliensis was 98.8 %. However, strain NRRL 5646(T) could be clearly distinguished from these Nocardia species based on DNA-DNA hybridization data. Consequently, strain NRRL 5646(T) is considered to represent a novel species of the genus Nocardia, for which the name Nocardia iowensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is NRRL 5646(T) (=UI 122540(T)=NRRL B-24671(T)=DSM 45197(T)).
Figures

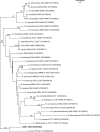
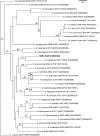
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

