Expression of apolipoprotein C-III in McA-RH7777 cells enhances VLDL assembly and secretion under lipid-rich conditions
- PMID: 19622837
- PMCID: PMC2789775
- DOI: 10.1194/M900346-JLR200
Expression of apolipoprotein C-III in McA-RH7777 cells enhances VLDL assembly and secretion under lipid-rich conditions
Abstract
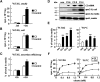
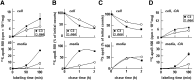
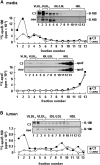
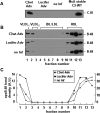
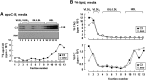
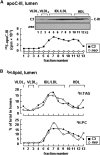
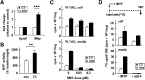
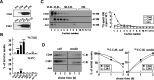
Apolipoprotein (apo) C-III plays a regulatory role in VLDL lipolysis and clearance. In this study, we determined a potential intracellular role of apoC-III in hepatic VLDL assembly and secretion. Stable expression of recombinant apoC-III in McA-RH7777 cells resulted in increased secretion efficiency of VLDL-associated triacylglycerol (TAG) and apoB-100 in a gene-dosage-dependent manner. The stimulatory effect of apoC-III on TAG secretion was manifested only when cells were cultured under lipid-rich (i.e., media supplemented with exogenous oleate) but not lipid-poor conditions. The stimulated TAG secretion was accompanied by increased secretion of apoB-100 and apoB-48 as VLDL(1). Expression of apoC-III also increased mRNA and activity of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP). Pulse-chase experiments showed that apoC-III expression promoted VLDL(1) secretion even under conditions where the MTP activity was inhibited immediately after the formation of lipid-poor apoB-100 particles, suggesting an involvement of apoC-III in the second-step VLDL assembly process. Consistent with this notion, the newly synthesized apoC-III was predominantly associated with TAG within the microsomal lumen that resembled lipid precursors of VLDL. Introducing an Ala23-to-Thr mutation into apoC-III, a naturally occurring mutation originally identified in two Mayan Indian subjects with hypotriglyceridemia, abolished the ability of apoC-III to stimulate VLDL secretion from transfected cells. Thus, expression of apoC-III in McA-RH7777 cells enhances hepatic TAG-rich VLDL assembly and secretion under lipid-rich conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Missense mutation in APOC3 within the C-terminal lipid binding domain of human ApoC-III results in impaired assembly and secretion of triacylglycerol-rich very low density lipoproteins: evidence that ApoC-III plays a major role in the formation of lipid precursors within the microsomal lumen.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 5;286(31):27769-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.203679. Epub 2011 Jun 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21676879 Free PMC article.
-
Human apolipoprotein C-III - a new intrahepatic protein factor promoting assembly and secretion of very low density lipoproteins.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Dec;12(2):133-40. doi: 10.2174/1871529x11202020133. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 23030451 Review.
-
Normal activity of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein is required for the oleate-induced secretion of very low density lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B from McA-RH7777 cells.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 9;272(19):12272-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.19.12272. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9139669
-
Apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein assembly in microsomal triglyceride transfer protein-deficient McA-RH7777 cells.J Lipid Res. 2010 Aug;51(8):2253-64. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M005371. Epub 2010 Feb 24. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20181985 Free PMC article.
-
[THE LIPOLYSIS IN PHYLOGENETICALLY EARLY LIPOPROTEINS OF LOW DENSITY AND MORE LATER LIPOPROTEINS OF VERY LOW DENSITY: FUNCTION AND DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF APOE AND APOC-III].Klin Lab Diagn. 2015 Dec;60(12):4-14. Klin Lab Diagn. 2015. PMID: 27032246 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Elevated Levels of Apolipoprotein CIII Increase the Risk of Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 23;12:646185. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.646185. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33967959 Free PMC article.
-
β-Carotene conversion to vitamin A delays atherosclerosis progression by decreasing hepatic lipid secretion in mice.J Lipid Res. 2020 Nov;61(11):1491-1503. doi: 10.1194/jlr.RA120001066. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 32963037 Free PMC article.
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease experiences accumulation of hepatic liquid crystal associated with increasing lipophagy.Cell Biosci. 2020 Apr 6;10:55. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00414-2. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32280452 Free PMC article.
-
Serum apolipoproteins and apolipoprotein-defined lipoprotein subclasses: a hypothesis-generating prospective study of cardiovascular events in T1D.J Lipid Res. 2019 Aug;60(8):1432-1439. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P090647. Epub 2019 Jun 15. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 31203233 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Effects of PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9) Inhibition and Statins on Postprandial Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Metabolism.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Jul;38(7):1644-1655. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.310882. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29880491 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Jong M. C., Hofker M. H., Havekes L. M. 1999. Role of ApoCs in lipoprotein metabolism: functional differences between ApoC1, ApoC2, and ApoC3. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 19: 472–484. - PubMed
-
- Cohn J. S., Tremblay M., Batal R., Jacques H., Rodriguez C., Steiner G., Mamer O., Davignon J. 2004. Increased apoC-III production is a characteristic feature of patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Atherosclerosis. 177: 137–145. - PubMed
-
- Zheng C., Khoo C., Ikewaki K., Sacks F. M. 2007. Rapid turnover of apolipoprotein C–III-containing triglyceride-rich lipoproteins contributing to the formation of LDL subfractions. J. Lipid Res. 48: 1190–1203. - PubMed
-
- Karathanasis S. K., Norum R. A., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. 1983. An inherited polymorphism in the human apolipoprotein A-I gene locus related to the development of atherosclerosis. Nature. 301: 718–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

