Expression of apolipoprotein C-III in McA-RH7777 cells enhances VLDL assembly and secretion under lipid-rich conditions
- PMID: 19622837
- PMCID: PMC2789775
- DOI: 10.1194/M900346-JLR200
Expression of apolipoprotein C-III in McA-RH7777 cells enhances VLDL assembly and secretion under lipid-rich conditions
Abstract
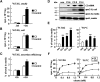
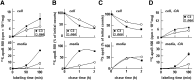
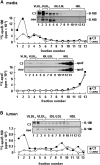
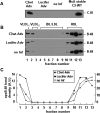
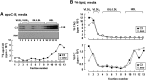
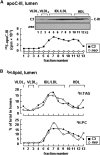
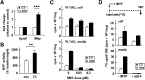
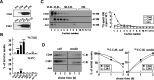
Apolipoprotein (apo) C-III plays a regulatory role in VLDL lipolysis and clearance. In this study, we determined a potential intracellular role of apoC-III in hepatic VLDL assembly and secretion. Stable expression of recombinant apoC-III in McA-RH7777 cells resulted in increased secretion efficiency of VLDL-associated triacylglycerol (TAG) and apoB-100 in a gene-dosage-dependent manner. The stimulatory effect of apoC-III on TAG secretion was manifested only when cells were cultured under lipid-rich (i.e., media supplemented with exogenous oleate) but not lipid-poor conditions. The stimulated TAG secretion was accompanied by increased secretion of apoB-100 and apoB-48 as VLDL(1). Expression of apoC-III also increased mRNA and activity of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP). Pulse-chase experiments showed that apoC-III expression promoted VLDL(1) secretion even under conditions where the MTP activity was inhibited immediately after the formation of lipid-poor apoB-100 particles, suggesting an involvement of apoC-III in the second-step VLDL assembly process. Consistent with this notion, the newly synthesized apoC-III was predominantly associated with TAG within the microsomal lumen that resembled lipid precursors of VLDL. Introducing an Ala23-to-Thr mutation into apoC-III, a naturally occurring mutation originally identified in two Mayan Indian subjects with hypotriglyceridemia, abolished the ability of apoC-III to stimulate VLDL secretion from transfected cells. Thus, expression of apoC-III in McA-RH7777 cells enhances hepatic TAG-rich VLDL assembly and secretion under lipid-rich conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Jong M. C., Hofker M. H., Havekes L. M. 1999. Role of ApoCs in lipoprotein metabolism: functional differences between ApoC1, ApoC2, and ApoC3. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 19: 472–484. - PubMed
-
- Cohn J. S., Tremblay M., Batal R., Jacques H., Rodriguez C., Steiner G., Mamer O., Davignon J. 2004. Increased apoC-III production is a characteristic feature of patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Atherosclerosis. 177: 137–145. - PubMed
-
- Zheng C., Khoo C., Ikewaki K., Sacks F. M. 2007. Rapid turnover of apolipoprotein C–III-containing triglyceride-rich lipoproteins contributing to the formation of LDL subfractions. J. Lipid Res. 48: 1190–1203. - PubMed
-
- Karathanasis S. K., Norum R. A., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. 1983. An inherited polymorphism in the human apolipoprotein A-I gene locus related to the development of atherosclerosis. Nature. 301: 718–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

