Effects of antenatal exposure to magnesium sulfate on neuroprotection and mortality in preterm infants: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 19622997
- PMCID: PMC2761069
- DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181ae98c2
Effects of antenatal exposure to magnesium sulfate on neuroprotection and mortality in preterm infants: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To review the evidence regarding neuroprotective effects of antenatal exposure to magnesium sulfate.
Data sources: We conducted database searches of MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library and Controlled Trials Register, as well as the ClinicalTrials.gov and International Clinical Trials Register websites. Bibliographies of all relevant articles were reviewed.
Methods of study selection: Randomized controlled trials comparing magnesium sulfate with placebo/other treatment in patients at risk of preterm delivery were evaluated for inclusion and methodological quality. The primary outcome was death or cerebral palsy by 18-24 months corrected age. Secondary outcomes were death, cerebral palsy, moderate-severe cerebral palsy, and death or moderate-severe cerebral palsy. Separate analyses were performed according to the gestational age (GA) at randomization (less than 32 to 34 weeks and less than 30 weeks) and for studies in which magnesium sulfate was used exclusively for fetal neuroprotection.
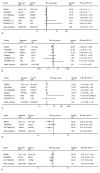
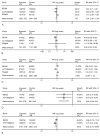
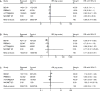
Tabulation, integration, and results: Five randomized controlled trials were included (5,235 fetuses/infants). When analyzed by GA at randomization, in utero exposure to magnesium sulfate at less than 32-34 weeks did not reduce the rate of death or cerebral palsy (relative risk [RR] 0.92, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.83-1.03). However, cerebral palsy (RR 0.70, 95% CI 0.55-0.89), moderate-severe cerebral palsy (RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.43-0.84), and death or moderate-severe cerebral palsy were significantly reduced, without an evident increase in the risk of death (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.89-1.14). Similar results were obtained when the GA at randomization was less than 30 weeks. When only neuroprotection trials (four trials, 4,324 fetuses/infants) are analyzed, in utero exposure to magnesium sulfate additionally reduced the primary outcome of death or cerebral palsy. The number needed to treat to prevent one case of cerebral palsy among those who survive until age 18-24 months is 46 (95% CI 26-187) in infants exposed to magnesium sulfate in utero before 30 weeks, and 56 (95% CI 34-164) in infants exposed to magnesium sulfate in utero before 32 to 34 weeks.
Conclusion: Fetal exposure to magnesium sulfate in women at risk of preterm delivery significantly reduces the risk of cerebral palsy without increasing the risk of death.
Figures
References
-
- Nelson KB, Grether JK. Can magnesium sulfate reduce the risk of cerebral palsy in very low birth weight infants? Pediatrics. 1995;95:263–9. - PubMed
-
- Yeargin-Allsopp M, Van Naarden Braun K, Doernberg NS, Benedict RE, Kirby RS, Durkin MS. Prevalence of cerebral palsy in 8-year-old children in three areas of the United States in 2002: a multisite collaboration. Pediatrics. 2008;121:547–54. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsson B, Hagberg G, Hagberg B, Ladfors L, Niklasson A, Hagberg H. Cerebral Palsy in preterm infants: a population-based case-control study of antenatal and intrapartal risk factors. Acta Paediatr. 2002;91:946–951. - PubMed
-
- Clark SM, Ghulmiyyah LM, Hankins GDV. Antenatal antecedents and the impact of obstetric care in the etiology of cerebral palsy. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2008;51:775–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HD36801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD019897/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27861/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040560/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27860/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034210/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD21414/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027905/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027861/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD53907/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34210/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD21410/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027869/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027917/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34116/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034122/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021414/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040485/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027860/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053097/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD34208/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040500/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040512/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD27917/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021410/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HD036801/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040545/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD40544/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

