Angiogenesis is associated with the onset of hyperplasia in human ductal breast disease
- PMID: 19623180
- PMCID: PMC2736809
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605196
Angiogenesis is associated with the onset of hyperplasia in human ductal breast disease
Abstract
Background: The precise timing of the angiogenic switch and the role of angiogenesis in the development of breast malignancy is currently unknown.
Methods: Therefore, the expression of CD31 (pan endothelial cells (ECs)), endoglin (actively proliferating ECs), hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1alpha), vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF) and tissue factor (TF) were quantified in 140 surgical specimens comprising normal human breast, benign and pre-malignant hyperplastic tissue, in situ and invasive breast cancer specimens.
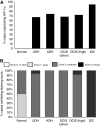
Results: Significant increases in angiogenesis (microvessel density) were observed between normal and benign hyperplastic breast tissue (P<0.005), and between in situ and invasive carcinomas (P<0.0005). In addition, significant increases in proliferating ECs were observed in benign hyperplastic breast compared with normal breast (P<0.05) cancers and in invasive compared with in situ cancers (P<0.005). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, VEGF and TF expression were significantly associated with increases in both angiogenesis and proliferating ECs (P<0.05). Moreover, HIF-1alpha was expressed by 60-75% of the hyperplastic lesions, and a significant association was observed between VEGF and TF in ECs (P<0.005) and invasive tumour cells (P<0.01).
Conclusions: These findings are the first to suggest that the angiogenic switch, associated with increases in HIF-1alpha, VEGF and TF expression, occurs at the onset of hyperplasia in the mammary duct, although the greatest increase in angiogenesis occurs with the development of invasion.
Figures


References
-
- Amarzguioui M, Peng Q, Wiiger MT, Vasovic V, Babaie E, Holen T, Nesland JM, Prydz H (2006) Ex vivo and in vivo delivery of anti-tissue factor short interfering RNA inhibits mouse pulmonary metastasis of B16 melanoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 12: 4055–4061 - PubMed
-
- Bergers G, Benjamin LE (2003) Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 401–410 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

