Type I interferon receptor controls B-cell expression of nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors and autoantibody production in a murine model of lupus
- PMID: 19624844
- PMCID: PMC2745794
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2771
Type I interferon receptor controls B-cell expression of nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors and autoantibody production in a murine model of lupus
Abstract
Introduction: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the production of high-titer IgG autoantibodies directed against nuclear autoantigens. Type I interferon (IFN-I) has been shown to play a pathogenic role in this disease. In the current study, we characterized the role of the IFNAR2 chain of the type I IFN (IFN-I) receptor in the targeting of nucleic acid-associated autoantigens and in B-cell expression of the nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors (TLRs), TLR7 and TLR9, in the pristane model of lupus.
Methods: Wild-type (WT) and IFNAR2-/- mice were treated with pristane and monitored for proteinuria on a monthly basis. Autoantibody production was determined by autoantigen microarrays and confirmed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunoprecipitation. Serum immunoglobulin isotype levels, as well as B-cell cytokine production in vitro, were quantified by ELISA. B-cell proliferation was measured by thymidine incorporation assay.
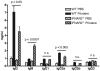
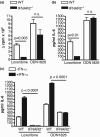
Results: Autoantigen microarray profiling revealed that pristane-treated IFNAR2-/- mice lacked autoantibodies directed against components of the RNA-associated autoantigen complexes Smith antigen/ribonucleoprotein (Sm/RNP) and ribosomal phosphoprotein P0 (RiboP). The level of IgG anti-single-stranded DNA and anti-histone autoantibodies in pristane-treated IFNAR2-/- mice was decreased compared to pristane-treated WT mice. TLR7 expression and activation by a TLR7 agonist were dramatically reduced in B cells from IFNAR2-/- mice. IFNAR2-/- B cells failed to upregulate TLR7 as well as TLR9 expression in response to IFN-I, and effector responses to TLR7 and TLR9 agonists were significantly decreased as compared to B cells from WT mice following treatment with IFN-alpha.
Conclusions: Our studies provide a critical link between the IFN-I pathway and the regulation of TLR-specific B-cell responses in a murine model of SLE.
Figures

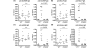
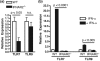
References
-
- Lovgren T, Eloranta ML, Kastner B, Wahren-Herlenius M, Alm GV, Ronnblom L. Induction of interferon-alpha by immune complexes or liposomes containing systemic lupus erythematosus autoantigen- and Sjogren's syndrome autoantigen-associated RNA. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1917–1927. doi: 10.1002/art.21893. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

