Clusters of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis cases, Europe
- PMID: 19624920
- PMCID: PMC2744220
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1507.080994
Clusters of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis cases, Europe
Abstract
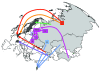
Molecular surveillance of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR TB) was implemented in Europe as case reporting in 2005. For all new MDR TB cases detected from January 2003 through June 2007, countries reported case-based epidemiologic data and DNA fingerprint patterns of MDR TB strains when available. International clusters were detected and analyzed. From 2003 through mid-2007 in Europe, 2,494 cases of MDR TB were reported from 24 European countries. Epidemiologic and molecular data were linked for 593 (39%) cases, and 672 insertion sequence 6110 DNA fingerprint patterns were reported from 19 countries. Of these patterns, 288 (43%) belonged to 18 European clusters; 7 clusters (242/288 cases, 84%) were characterized by strains of the Beijing genotype family, including the largest cluster (175/288 cases, 61%). Both clustering and the Beijing genotype were associated with strains originating in eastern European countries. Molecular cluster detection contributes to identification of transmission profile, risk factors, and control measures.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Anti-tuberculosis drug resistance in the world. Fourth global report. WHO/HTM/TB/Geneva; 2008.394.
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Geneva: The Organization; 2006. [cited 2009 May 26]. Available from http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241546956_eng.pdf
-
- Gandhi NR, Moll A, Sturm AW, Pawinski R, Govender T, Lalloo U, et al. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis as a cause of death in patients co-infected with tuberculosis and HIV in a rural area of South Africa. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
