Human cytomegalovirus UL28 and UL29 open reading frames encode a spliced mRNA and stimulate accumulation of immediate-early RNAs
- PMID: 19625400
- PMCID: PMC2748044
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00396-09
Human cytomegalovirus UL28 and UL29 open reading frames encode a spliced mRNA and stimulate accumulation of immediate-early RNAs
Abstract
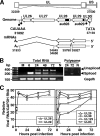
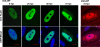
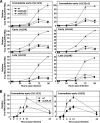
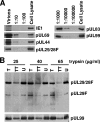
We have identified a spliced transcript that contains sequences from the HCMV UL29 and UL28 open reading frames. It contains amino-terminal UL29 sequences followed by UL28 sequences, and it includes a poly(A) signal derived from the 3'-untranslated region following the UL26 open reading frame. UL29/28 RNA is expressed with early kinetics, and a virus containing a FLAG epitope inserted at the amino terminus of UL29 expressed a tagged approximately 79-kDa protein, pUL29/28, that was detected at 6 h postinfection. The virus also expressed a less-abundant tagged 41-kDa protein, which corresponds in size to a protein that could be produced by translation of an unspliced UL29/28 transcript. Consistent with this prediction, both unspliced and spliced UL29/28 transcript was present in RNA isolated from polysomes. FLAG-tagged protein from the UL29/28 locus accumulated within nuclear viral replication centers during the early phase of infection. Late after infection it was present in the cytoplasm as well, and the protein was present and resistant to proteinase treatment in partially purified preparations of viral particles. Disruption of the UL29/28 locus by mutation resulted in a 10-fold decrease in the levels of DNA replication along with a similar reduction in virus yield. Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR analysis revealed an approximately 2-fold decrease in immediate-early gene expression at 4 to 10 h postinfection compared to the wild-type virus, and transient expression of pUL29/28 activated the major immediate-early promoter. Our results argue that the UL29/28 locus contributes to activation of immediate-early gene expression.
Figures



References
-
- Bowen, N. J., N. Fujita, M. Kajita, and P. A. Wade. 2004. Mi-2/NuRD: multiple complexes for many purposes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1677:52-57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

