Evolution of teleost fish retroviruses: characterization of new retroviruses with cellular genes
- PMID: 19625413
- PMCID: PMC2748043
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02546-08
Evolution of teleost fish retroviruses: characterization of new retroviruses with cellular genes
Abstract
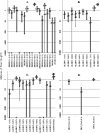
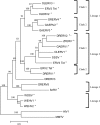
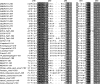
The interactions between retroviruses and their hosts can be of a beneficial or detrimental nature. Some endogenous retroviruses are involved in development, while others cause disease. The Genome Parsing Suite (GPS) is a software tool to track and trace all Retroid agents in any sequenced genome (M. A. McClure et al., Genomics 85:512-523, 2005). Using the GPS, the retroviral content was assessed in four model teleost fish. Eleven new species of fish retroviruses are identified and characterized. The reverse transcriptase protein sequences were used to reconstruct a fish retrovirus phylogeny, thereby, significantly expanding the epsilon-retrovirus family. Most of these novel retroviruses encode additional genes, some of which are homologous to cellular genes that would confer viral advantage. Although the fish divergence is much more ancient, retroviruses began infecting fish genomes approximately 4 million years ago.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human endogenous retrovirus type I-related viruses have an apparently widespread distribution within vertebrates.J Virol. 1997 Jan;71(1):437-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.1.437-443.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 8985368 Free PMC article.
-
Marine origin of retroviruses in the early Palaeozoic Era.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 10;8:13954. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13954. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28071651 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence relationships of type D retroviruses which cause simian acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):317-29. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90274-1. Virology. 1987. PMID: 2435057
-
Origins and evolutionary relationships of retroviruses.Q Rev Biol. 1989 Mar;64(1):1-30. doi: 10.1086/416128. Q Rev Biol. 1989. PMID: 2469098 Review.
-
Molecular biology of type A endogenous retrovirus.Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1990 Sep;63(2-3):77-90. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1990. PMID: 1710682 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous Retroviruses in Fish Genomes: From Relics of Past Infections to Evolutionary Innovations?Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 9;7:1197. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01197. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27555838 Free PMC article.
-
Pushing the endogenous envelope.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Aug 12;368(1626):20120506. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0506. Print 2013 Sep 19. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23938755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A single inactivating amino acid change in the SARS-CoV-2 NSP3 Mac1 domain attenuates viral replication and pathogenesis in vivo.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 10:2023.04.18.537104. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.18.537104. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 31;19(8):e1011614. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011614. PMID: 37131711 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Mobile Elements in Ray-Finned Fish Genomes.Life (Basel). 2020 Sep 25;10(10):221. doi: 10.3390/life10100221. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unique Structure and Distinctive Properties of the Ancient and Ubiquitous Gamma-Type Envelope Glycoprotein.Viruses. 2023 Jan 18;15(2):274. doi: 10.3390/v15020274. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851488 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alfaro, M. 2003. Bayes or bootstrap? A simulation study comparing the performance of Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling and bootstrapping in assessing phylogenetic confidence. Mol. Biol. Evol. 20:255-266. - PubMed
-
- Alfaro, M. E., and M. T. Holder. 2006. The posterior and the prior in Bayesian phylogenetics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 37:19-42.
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

