Importin beta regulates the seeding of chromatin with initiation sites for nuclear pore assembly
- PMID: 19625448
- PMCID: PMC2743622
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-02-0150
Importin beta regulates the seeding of chromatin with initiation sites for nuclear pore assembly
Abstract
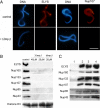
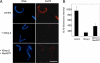
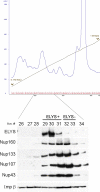
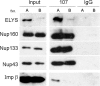
The nuclear envelope of higher eukaryotic cells reforms at the exit from mitosis, in concert with the assembly of nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). The first step in postmitotic NPC assembly involves the "seeding" of chromatin with ELYS and the Nup107-160 complex. Subsequent steps in the assembly process are poorly understood and different mechanistic models have been proposed to explain the formation of the full supramolecular structure. Here, we show that the initial step of chromatin seeding is negatively regulated by importin beta. Direct imaging of the chromatin attachment sites reveals single sites situated predominantly on the highest substructures of chromatin surface and lacking any sign of annular structures or oligomerized pre-NPCs. Surprisingly, the inhibition by importin beta is only partially reversed by RanGTP. Importin beta forms a high-molecular-weight complex with both ELYS and the Nup107-160 complex in cytosol. We suggest that initiation sites for NPC assembly contain single copies of chromatin-bound ELYS/Nup107-160 and that the lateral oligomerization of these subunits depends on the recruitment of membrane components. We predict that additional regulators, besides importin beta and Ran, may be involved in coordinating the initial seeding of chromatin with subsequent steps in the NPC assembly pathway.
Figures




Comment in
- Mol Biol Cell. 20:3985.
Similar articles
-
Transportin regulates major mitotic assembly events: from spindle to nuclear pore assembly.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Sep;20(18):4043-58. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-02-0152. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19641022 Free PMC article.
-
Importin beta negatively regulates nuclear membrane fusion and nuclear pore complex assembly.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Nov;14(11):4387-96. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-05-0275. Epub 2003 Aug 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14551248 Free PMC article.
-
RanGTP mediates nuclear pore complex assembly.Nature. 2003 Aug 7;424(6949):689-94. doi: 10.1038/nature01898. Epub 2003 Jul 30. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12894213
-
Spatial and temporal control of nuclear envelope assembly by Ran GTPase.Symp Soc Exp Biol. 2004;(56):193-204. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 2004. PMID: 15565882 Review.
-
The Role of Nucleoporin Elys in Nuclear Pore Complex Assembly and Regulation of Genome Architecture.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 13;21(24):9475. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249475. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33322130 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The nuclear envelope in the plant cell cycle: structure, function and regulation.Ann Bot. 2011 May;107(7):1111-8. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcq268. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Ann Bot. 2011. PMID: 21239406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, Maintenance, and Regulation of Nuclear Pore Complexes: The Gatekeepers of the Eukaryotic Genome.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022 Mar 1;14(3):a040691. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a040691. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022. PMID: 34312247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Karyopherin alpha2 is essential for rRNA transcription and protein synthesis in proliferative keratinocytes.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 3;8(10):e76416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076416. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098495 Free PMC article.
-
Repo-Man-PP1: a link between chromatin remodelling and nuclear envelope reassembly.Nucleus. 2012 Mar 1;3(2):138-42. doi: 10.4161/nucl.19267. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Nucleus. 2012. PMID: 22555598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interaction of Epac1 and Ran promotes Rap1 activation at the nuclear envelope.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;30(16):3956-69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00242-10. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20547757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alber F., et al. The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature. 2007;450:695–701. - PubMed
-
- Allen N. P., Patel S. S., Huang L., Chalkley R. J., Burlingame A., Lutzmann M., Hurt E. C., Rexach M. Deciphering networks of protein interactions at the nuclear pore complex. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2002;1:930–946. - PubMed
-
- Allen T. D., Rutherford S. A., Murray S., Sanderson H. S., Gardiner F., Kiseleva E., Goldberg M. W., Drummond S. P. A protocol for isolating Xenopus oocyte nuclear envelope for visualization and characterization by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) or transmission electron microscopy (TEM) Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:1166–1172. - PubMed
-
- Antonin W., Ellenberg J., Dultz E. Nuclear pore complex assembly through the cell cycle: regulation and membrane organization. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:2004–2016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

