Antibody limits in vivo murid herpesvirus-4 replication by IgG Fc receptor-dependent functions
- PMID: 19625459
- PMCID: PMC2885036
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.014266-0
Antibody limits in vivo murid herpesvirus-4 replication by IgG Fc receptor-dependent functions
Abstract
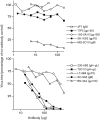
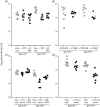
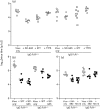
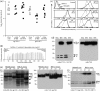
Antibody is an important antiviral defence. However, it is considered to do little against human gamma-herpesviruses, which establish predominantly latent infections regulated by T cells. One limitation on analysing these infections has been that latency is already well-established at clinical presentation; early infection may still be accessible to antibody. Here, using murid herpesvirus-4 (MuHV-4), we tested the impact of adoptively transferred antibody on early gamma-herpesvirus infection. Immune sera and neutralizing and non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) all reduced acute lytic MuHV-4 replication. The reductions, even by neutralizing mAbs, were largely or completely dependent on host IgG Fc receptors. Therefore, passive antibody can blunt acute gamma-herpesvirus lytic infection, and does this principally by IgG Fc-dependent functions rather than by neutralization.
Figures



References
-
- Callan, M. F., Steven, N., Krausa, P., Wilson, J. D., Moss, P. A., Gillespie, G. M., Bell, J. I., Rickinson, A. B. & McMichael, A. J. (1996). Large clonal expansions of CD8+ T cells in acute infectious mononucleosis. Nat Med 2, 906–911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

