Decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor depends on amyloid aggregation state in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19625522
- PMCID: PMC3411546
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4736-08.2009
Decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor depends on amyloid aggregation state in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
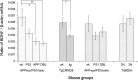
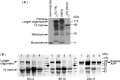
Downregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the cortex occurs early in the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Since BDNF plays a critical role in neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and memory, BDNF reduction may contribute to synaptic and cellular loss and memory deficits characteristic of AD. In vitro evidence suggests that amyloid-beta (A beta) contributes to BDNF downregulation in AD, but the specific A beta aggregation state responsible for this downregulation in vivo is unknown. In the present study, we examined cortical levels of BDNF mRNA in three different transgenic AD mouse models harboring mutations in APP resulting in A beta overproduction, and in a genetic mouse model of Down syndrome. Two of the three A beta transgenic strains (APP(NLh) and TgCRND8) exhibited significantly decreased cortical BDNF mRNA levels compared with wild-type mice, whereas neither the other strain (APP(swe)/PS-1) nor the Down syndrome mouse model (Ts65Dn) was affected. Only APP(NLh) and TgCRND8 mice expressed high A beta(42)/A beta(40) ratios and larger SDS-stable A beta oligomers (approximately 115 kDa). TgCRND8 mice exhibited downregulation of BDNF transcripts III and IV; transcript IV is also downregulated in AD. Furthermore, in all transgenic mouse strains, there was a correlation between levels of large oligomers, A beta(42)/A beta(40), and severity of BDNF decrease. These data show that the amount and species of A beta vary among transgenic mouse models of AD and are negatively correlated with BDNF levels. These findings also suggest that the effect of A beta on decreased BDNF expression is specific to the aggregation state of A beta and is dependent on large oligomers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture decreases cognitive impairment and promotes neurogenesis in the APP/PS1 transgenic mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jan 22;14:37. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-37. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24447795 Free PMC article.
-
Differential deregulation of NGF and BDNF neurotrophins in a transgenic rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2017 Dec;108:307-323. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.08.019. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Neurobiol Dis. 2017. PMID: 28865749
-
Novel Phenylethanoid Glycosides Improve Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity via the Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate-CREB-Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Growth Factor Pathway in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice.Gerontology. 2023;69(9):1065-1075. doi: 10.1159/000531194. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Gerontology. 2023. PMID: 37285833 Free PMC article.
-
Lamotrigine attenuates deficits in synaptic plasticity and accumulation of amyloid plaques in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Dec;35(12):2713-2725. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 25044076
-
In vitro validation of effects of BDNF-expressing mesenchymal stem cells on neurodegeneration in primary cultured neurons of APP/PS1 mice.Neuroscience. 2015 Oct 29;307:37-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26297896
Cited by
-
Combination of Aβ clearance and neurotrophic factors as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease.Neurosci Bull. 2013 Feb;29(1):111-20. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1287-6. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Neurosci Bull. 2013. PMID: 23179066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotrophins role in depression neurobiology: a review of basic and clinical evidence.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011 Dec;9(4):530-52. doi: 10.2174/157015911798376262. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22654714 Free PMC article.
-
Synapse-binding subpopulations of Aβ oligomers sensitive to peptide assembly blockers and scFv antibodies.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012 Nov 21;3(11):972-81. doi: 10.1021/cn300122k. Epub 2012 Oct 23. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23173076 Free PMC article.
-
How does apolipoprotein E genotype influence the relationship between physical activity and Alzheimer's disease risk? A novel integrative model.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Jan 27;15(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01170-4. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 36707869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF inhibits neurodegenerative disease-associated asparaginyl endopeptidase activity via phosphorylation by AKT.JCI Insight. 2018 Aug 23;3(16):e99007. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.99007. eCollection 2018 Aug 23. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30135302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ando S, Kobayashi S, Waki H, Kon K, Fukui F, Tadenuma T, Iwamoto M, Takeda Y, Izumiyama N, Watanabe K, Nakamura H. Animal model of dementia induced by entorhinal synaptic damage and partial restoration of cognitive deficits by BDNF and carnitine. J Neurosci Res. 2002;70:519–527. - PubMed
-
- Bellucci A, Luccarini I, Scali C, Prosperi C, Giovannini MG, Pepeu G, Casamenti F. Cholinergic dysfunction, neuronal damage and axonal loss in TgCRND8 mice. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;23:260–272. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS. Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1997;19:939–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
