The paralogous genes RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1 and SIMILAR TO RCD ONE1 have partially redundant functions during Arabidopsis development
- PMID: 19625634
- PMCID: PMC2736012
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.142786
The paralogous genes RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1 and SIMILAR TO RCD ONE1 have partially redundant functions during Arabidopsis development
Erratum in
- Plant Physiol. 2009 Oct;151(2):966
Abstract
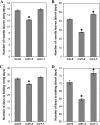
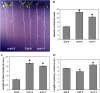
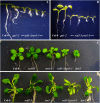
RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1 (RCD1) and SIMILAR TO RCD ONE1 (SRO1) are the only two proteins encoded in the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) genome containing both a putative poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase catalytic domain and a WWE protein-protein interaction domain, although similar proteins have been found in other eukaryotes. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases mediate the attachment of ADP-ribose units from donor NAD(+) molecules to target proteins and have been implicated in a number of processes, including DNA repair, apoptosis, transcription, and chromatin remodeling. We have isolated mutants in both RCD1 and SRO1, rcd1-3 and sro1-1, respectively. rcd1-3 plants display phenotypic defects as reported for previously isolated alleles, most notably reduced stature. In addition, rcd1-3 mutants display a number of additional developmental defects in root architecture and maintenance of reproductive development. While single mutant sro1-1 plants are relatively normal, loss of a single dose of SRO1 in the rcd1-3 background increases the severity of several developmental defects, implying that these genes do share some functions. However, rcd1-3 and sro1-1 mutants behave differently in several developmental events and abiotic stress responses, suggesting that they also have distinct functions. Remarkably, rcd1-3; sro1-1 double mutants display severe defects in embryogenesis and postembryonic development. This study shows that RCD1 and SRO1 are at least partially redundant and that they are essential genes for plant development.
Figures





Comment in
-
Radical-induced cell death1 and similar to RCD one1 and the stress-induced morphogenetic response.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Feb;5(2):143-5. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.2.10400. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20009514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams-Phillips L, Wan J, Tan X, Dunning FM, Meyers BC, Michelmore RW, Bent AF (2008) Discovery of ADP-ribosylation and other plant defense pathway elements through expression profiling of four different Arabidopsis-Pseudomonas R-avr interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21 646–657 - PubMed
-
- Aguiar RC, Takeyama K, He C, Kreinbrink K, Shipp MA (2005) B-aggressive lymphoma family proteins have unique domains that modulate transcription and exhibit poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity. J Biol Chem 280 33756–33765 - PubMed
-
- Aguiar RC, Yakushijin Y, Kharbanda S, Salgia R, Fletcher JA, Shipp MA (2000) BAL is a novel risk-related gene in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas that enhances cellular migration. Blood 96 4328–4334 - PubMed
-
- Ahlfors R, Lang S, Overmyer K, Jaspers P, Brosche M, Tauriainen A, Kollist H, Tuominen H, Belles-Boix E, Piippo M, et al (2004) Arabidopsis RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1 belongs to the WWE protein-protein interaction domain protein family and modulates abscisic acid, ethylene, and methyl jasmonate responses. Plant Cell 16 1925–1937 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

