A robust xenotransplantation model for acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 19626050
- PMCID: PMC3659827
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2009.143
A robust xenotransplantation model for acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
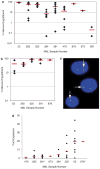
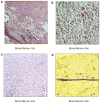
Xenotransplantation of human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in immunocompromised animals has been critical for defining leukemic stem cells. However, existing immunodeficient strains of mice have short life spans and low levels of AML cell engraftment, hindering long-term evaluation of primary human AML biology. A recent study suggested that NOD/LtSz-scid IL2Rgammac null (NSG) mice have enhanced AML cell engraftment, but this relied on technically challenging neonatal injections. Here, we performed extensive analysis of AML engraftment in adult NSG mice using tail vein injection. Of the 35 AML samples analyzed, 66% showed bone marrow engraftment over 0.1%. Further, 37% showed high levels of engraftment (>10%), with some as high as 95%. A 2-44-fold expansion of AML cells was often seen. Secondary and tertiary recipients showed consistent engraftment, with most showing further AML cell expansion. Engraftment did not correlate with French-American-British subtype or cytogenetic abnormalities. However, samples with FLT3 mutations showed a higher probability of engraftment than FLT3 wild type. Importantly, animals developed organomegaly and a wasting illness consistent with advanced leukemia. We conclude that the NSG xenotransplantation model is a robust model for human AML cell engraftment, which will allow better characterization of AML biology and testing of new therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Carroll has received research support from Sanofi Aventis Corporation.
Figures


References
-
- Ailles LE, Gerhard B, Kawagoe H, Hogge DE. Growth characteristics of acute myelogenous leukemia progenitors that initiate malignant hematopoiesis in nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient mice. Blood. 1999;94:1761–1772. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 1997;3:730–737. - PubMed
-
- Lapidot T, Fajerman Y, Kollet O. Immune-deficient SCID and NOD/SCID mice models as functional assays for studying normal and malignant human hematopoiesis. J Mol Med. 1997;75:664–673. - PubMed
-
- Christianson SW, Greiner DL, Hesselton RA, Leif JH, Wagar EJ, Schweitzer IB, et al. Enhanced human CD4+ T cell engraftment in beta2-microglobulin-deficient NOD-scid mice. J Immunol. 1997;158:3578–3586. - PubMed
-
- Shultz LD, Schweitzer PA, Christianson SW, Gott B, Schweitzer IB, Tennent B, et al. Multiple defects in innate and adaptive immunologic function in NOD/LtSz-scid mice. J Immunol. 1995;154:180–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

