Ligand-induced changes in the structure and dynamics of Escherichia coli peptide deformylase
- PMID: 19627112
- PMCID: PMC2881472
- DOI: 10.1021/bi900600b
Ligand-induced changes in the structure and dynamics of Escherichia coli peptide deformylase
Abstract
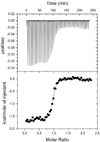
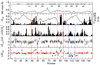
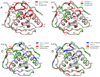
Peptide deformylase (PDF) is an enzyme that is responsible for removing the formyl group from nascently synthesized polypeptides in bacteria, attracting much attention as a potential target for novel antibacterial agents. Efforts to develop potent inhibitors of the enzyme have progressed on the basis of classical medicinal chemistry, combinatorial chemistry, and structural approaches, yet the validity of PDF as an antibacterial target hangs, in part, on the ability of inhibitors to selectively target this enzyme in favor of structurally related metallohydrolases. We have used (15)N NMR spectroscopy and isothermal titration calorimetry to investigate the high-affinity interaction of EcPDF with actinonin, a naturally occurring potent EcPDF inhibitor. Backbone amide chemical shifts, residual dipolar couplings, hydrogen-deuterium exchange, and (15)N relaxation reveal structural and dynamic effects of ligand binding in the immediate vicinity of the ligand-binding site as well as at remote sites. A comparison of the crystal structures of free and actinonin-bound EcPDF with the solution data suggests that most of the consequences of the ligand binding to the protein are lost or obscured during crystallization. The results of these studies improve our understanding of the thermodynamic global minimum and have important implications for structure-based drug design.
Figures
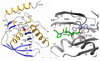
Similar articles
-
Ligand and Structure-Based Approaches for the Identification of Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors as Antibacterial Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 15;17(7):1141. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071141. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27428963 Free PMC article.
-
Delineation of alternative conformational states in Escherichia coli peptide deformylase via thermodynamic studies for the binding of actinonin.Biochemistry. 2009 Feb 24;48(7):1584-94. doi: 10.1021/bi8019542. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19191548 Free PMC article.
-
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of peptide deformylase (PDF) from Bacillus cereus in ligand-free and actinonin-bound forms.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2005 Jan 1;61(Pt 1):150-2. doi: 10.1107/S1744309104032440. Epub 2004 Dec 24. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2005. PMID: 16508119 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of peptide deformylase from Staphylococcus aureus in complex with actinonin, a naturally occurring antibacterial agent.Proteins. 2004 Nov 15;57(3):639-42. doi: 10.1002/prot.20231. Proteins. 2004. PMID: 15382235 No abstract available.
-
Bacterial Peptide deformylase inhibitors: a new class of antibacterial agents.Curr Med Chem. 2005;12(14):1607-21. doi: 10.2174/0929867054367194. Curr Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16022661 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-coding nucleotides and amino acids near the active site regulate peptide deformylase expression and inhibitor susceptibility in Chlamydia trachomatis.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Sep;157(Pt 9):2569-2581. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.049668-0. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 21719536 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro phosphorylation of the focal adhesion targeting domain of focal adhesion kinase by Src kinase.Biochemistry. 2012 Mar 20;51(11):2213-23. doi: 10.1021/bi300123a. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22372511 Free PMC article.
-
Trapping conformational states along ligand-binding dynamics of peptide deformylase: the impact of induced fit on enzyme catalysis.PLoS Biol. 2011 May;9(5):e1001066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001066. Epub 2011 May 24. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21629676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meinnel T, Blanquet S, Dardel F. A new subclass of the zinc metalloproteases superfamily revealed by the solution structure of peptide deformylase. J Mol Biol. 1996;262:375–386. - PubMed
-
- Meinnel T, Lazennec C, Villoing S, Blanquet S. Structure-function relationships within the peptide deformylase family. Evidence for a conserved architecture of the active site involving three conserved motifs and a metal ion. J Mol Biol. 1997;267:749–761. - PubMed
-
- Rajagopalan PT, Datta A, Pei D. Purification, characterization, and inhibition of peptide deformylase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1997;36:13910–13918. - PubMed
-
- Rajagopalan PTR, Yu XC, Pei D. Peptide deformylase: a new type of mononuclear iron protein. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119:12418–12419.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

