Oligomerization route to Py-Im polyamide macrocycles
- PMID: 19627138
- PMCID: PMC2736337
- DOI: 10.1021/ol901311m
Oligomerization route to Py-Im polyamide macrocycles
Abstract
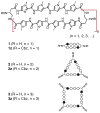
Cyclic eight-ring pyrrole-imidazole polyamides are sequence-specific DNA-binding small molecules that are cell permeable and can regulate endogenous gene expression. Syntheses of cyclic polyamides have been achieved by solid-phase and solution-phase methods. A rapid solution-phase oligomerization approach to eight-ring symmetrical cyclic polyamides yields 12- and 16-membered macrocycles as well. A preference for DNA binding by the 8- and 16-membered oligomers was observed over the 12-ring macrocycle, which we attributed to a conformational constraint not present in the smaller and larger systems.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Binding of hairpin pyrrole and imidazole polyamides to DNA: relationship between torsion angle and association rate constants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11510-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks897. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23042247 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic pyrrole-imidazole polyamides targeted to the androgen response element.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 May 27;131(20):7182-8. doi: 10.1021/ja901309z. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19413319 Free PMC article.
-
Fully automated synthesis of DNA-binding Py-Im polyamides using a triphosgene coupling strategy.Org Lett. 2015 Jan 2;17(1):158-61. doi: 10.1021/ol503388a. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Org Lett. 2015. PMID: 25496317
-
Sequence-specific DNA binding Pyrrole-imidazole polyamides and their applications.Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 May 1;26(8):1393-1411. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.01.026. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29439914 Review.
-
Synthesis and biological properties of sequence-specific DNA-alkylating pyrrole-imidazole polyamides.Acc Chem Res. 2006 Dec;39(12):935-44. doi: 10.1021/ar030287f. Acc Chem Res. 2006. PMID: 17176032 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition of nucleic acid junctions using triptycene-based molecules.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014 Dec 8;53(50):13746-50. doi: 10.1002/anie.201407061. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014. PMID: 25257803 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiometric Determination of Acid Dissociation Constants (pK a) for an Anticancer Pyrrole-Imidazole Polyamide.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022 Oct 26;13(11):1739-1744. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00348. eCollection 2022 Nov 10. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 36385938 Free PMC article.
-
Triptycene-based small molecules modulate (CAG)·(CTG) repeat junctions.Chem Sci. 2015 Aug 14;6(8):4752-4755. doi: 10.1039/c5sc01595b. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 26366282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dervan PB. Bioorg Med Chem. 2001;9:2215–2235. - PubMed
-
- Dervan PB, Edelson BS. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003;13:284–299. - PubMed
-
- Trauger JW, Baird EE, Dervan PB. Nature. 1996;382:559–561. - PubMed
- White S, Szewczyk JW, Turner JM, Baird EE, Dervan PB. Nature. 1998;391:468–470. - PubMed
- Kielkopf CL, Baird EE, Dervan PB, Rees DC. Nat Struct Biol. 1998;5:104–109. - PubMed
- Kielkopf CL, White S, Szewczyk JW, Turner JM, Baird EE, Dervan PB, Rees DC. Science. 1998;282:111–115. - PubMed
-
- Belitsky JM, Leslie SJ, Arora PS, Beerman TA, Dervan PB. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002;10:3313–3318. - PubMed
- Crowley KS, Phillion DP, Woodard SS, Scheitzer BA, Singh M, Shabany H, Burnette B, Hippenmeyer P, Heitmeier M, Bashkin JK. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003;13:1565–1570. - PubMed
- Best TP, Edelson BS, Nickols NG, Dervan PB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:12063–12068. - PMC - PubMed
- Edelson BS, Best TP, Olenyuk B, Nickols NG, Doss RM, Foister S, Heckel A, Dervan PB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:2802–2818. - PMC - PubMed
- Xiao X, Yu P, Lim HS, Sikder D, Kodadek T. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007;46:2865–2868. - PubMed
- Nickols NG, Jacobs CS, Farkas ME, Dervan PB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:363–370. - PMC - PubMed
- Dose C, Farkas ME, Chenoweth DM, Dervan PB. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:6859–6866. - PMC - PubMed
- Hsu CF, Dervan PB. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008;18:5851–5855. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

