False discovery rates of protein identifications: a strike against the two-peptide rule
- PMID: 19627159
- PMCID: PMC3398614
- DOI: 10.1021/pr9004794
False discovery rates of protein identifications: a strike against the two-peptide rule
Abstract
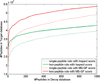
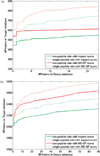
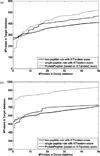
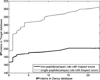
Most proteomics studies attempt to maximize the number of peptide identifications and subsequently infer proteins containing two or more peptides as reliable protein identifications. In this study, we evaluate the effect of this "two-peptide" rule on protein identifications, using multiple search tools and data sets. Contrary to the intuition, the "two-peptide" rule reduces the number of protein identifications in the target database more significantly than in the decoy database and results in increased false discovery rates, compared to the case when single-hit proteins are not discarded. We therefore recommend that the "two-peptide" rule should be abandoned, and instead, protein identifications should be subject to the estimation of error rates, as is the case with peptide identifications. We further extend the generating function approach (originally proposed for evaluating matches between a peptide and a single spectrum) to evaluating matches between a protein and an entire spectral data set.
Figures
Similar articles
-
False Discovery Rate Estimation for Hybrid Mass Spectral Library Search Identifications in Bottom-up Proteomics.J Proteome Res. 2019 Sep 6;18(9):3223-3234. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00863. Epub 2019 Aug 14. J Proteome Res. 2019. PMID: 31364354 Free PMC article.
-
MUDE: a new approach for optimizing sensitivity in the target-decoy search strategy for large-scale peptide/protein identification.J Proteome Res. 2010 May 7;9(5):2265-77. doi: 10.1021/pr901023v. J Proteome Res. 2010. PMID: 20199108
-
Spectral probabilities and generating functions of tandem mass spectra: a strike against decoy databases.J Proteome Res. 2008 Aug;7(8):3354-63. doi: 10.1021/pr8001244. Epub 2008 Jul 3. J Proteome Res. 2008. PMID: 18597511 Free PMC article.
-
Current algorithmic solutions for peptide-based proteomics data generation and identification.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013 Feb;24(1):31-8. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23142544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Verification of single-peptide protein identifications by the application of complementary database search algorithms.J Biomol Tech. 2006 Dec;17(5):327-32. J Biomol Tech. 2006. PMID: 17122065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabidiol and Tetrahydrocannabinol Antinociceptive Activity is Mediated by Distinct Receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans.Neurochem Res. 2024 Apr;49(4):935-948. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04069-6. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38141130
-
Identification of cross-reactive IgE-binding proteins from Philippine allergenic grass pollen extracts.Asia Pac Allergy. 2024 Aug;14(3):108-117. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.0000000000000155. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Asia Pac Allergy. 2024. PMID: 39220572 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Differential Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease by Integrating ELISA and Mass Spectrometry-Based Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;67(2):639-651. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180855. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 30614806 Free PMC article.
-
Cannflavins isolated from Cannabis sativa impede Caenorhabditis elegans response to noxious heat.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;397(1):535-548. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02621-3. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37480489
-
Anandamide Modulates Thermal Avoidance in Caenorhabditis elegans Through Vanilloid and Cannabinoid Receptor Interplay.Neurochem Res. 2024 Sep;49(9):2423-2439. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04186-w. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38847909
References
-
- Aebersold R, Mann M. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature. 2003;422:198–207. - PubMed
-
- Cargile BJ, Bundy JL, Stephenson JL., Jr Potential for false positive identifications from large databases through tandem mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2004;3:1082–1085. - PubMed
-
- Elias JE, Gygi SP. Target-decoy search strategy for increased confidence in large-scale protein identifications by mass spectrometry. Nat. Methods. 2007;4:207–214. - PubMed
-
- Kall L, Storey JD, MacCoss MJ, Noble SW. Assigning significance to peptides identified by tandem mass spectrometry using decoy databases. J. Proteome Res. 2008;7:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Omenn GS, States DJ, Adamski M, Blackwell TW, Menon R, Hermjakob H, Apweiler R, Haab BB, Simpson RJ, Eddes JS. Overview of the HUPO Plasma Proteome Project: results from the pilot phase with 35 collaborating laboratories and multiple analytical groups, generating a core dataset of 3020 proteins and a publicly-available database. Proteomics. 2005;5:3226–3245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

