Allylmethylsulfide Down-Regulates X-Ray Irradiation-Induced Nuclear Factor-kappaB Signaling in C57/BL6 Mouse Kidney
- PMID: 19627202
- PMCID: PMC6469522
- DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2008.1073
Allylmethylsulfide Down-Regulates X-Ray Irradiation-Induced Nuclear Factor-kappaB Signaling in C57/BL6 Mouse Kidney
Abstract
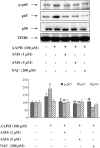
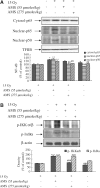
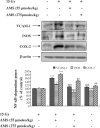
Allylmethylsulfide (AMS), a volatile organosulfur derivative from garlic, has been shown to have radioprotective effects in radiation-challenged cell and animal models, but the mechanism of radioprotection is not well understood. To determine the mechanism of radioprotection in an in vivo model, we first verified the antioxidant capacity of AMS using 2,2'-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride-induced human embryonic kidney 293T cells by measuring reactive oxygen species generation, reduced glutathione, protein tyrosine kinase/protein tyrosine phosphatase balance, and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) protein levels. We then investigated the protective effects of AMS (55 and 275 micromol/kg, intraperitoneal treatment) on 15 Gy X-ray-irradiated mouse kidney. The results showed that AMS decreased the free radical-induced lipid peroxidation in mice exposed to X-rays. Moreover, the antioxidative AMS suppressed the activation of NF-kappaB and its dependent genes such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and cyclooxygenase-2 through inhibition of IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and activation of IkappaB kinase alpha/beta and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Based on these results, AMS may be a useful radioprotective agent by down-regulating the MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathway that can be induced via X-ray irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Allylmethylsulfide, a Sulfur Compound Derived from Garlic, Attenuates Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 11;2020:7856318. doi: 10.1155/2020/7856318. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32617142 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects and molecular mechanisms of garlic organosulfur compounds on the production of inflammatory mediators.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Nov;57(11):2049-60. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201200843. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013. PMID: 23766070
-
Dietary grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit UVB-induced oxidative stress and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in in vivo SKH-1 hairless mice.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):995-1005. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0661. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17363493
-
Modulation of NF-κB and FOXOs by baicalein attenuates the radiation-induced inflammatory process in mouse kidney.Free Radic Res. 2011 May;45(5):507-17. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2011.555479. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Free Radic Res. 2011. PMID: 21284490
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Gastroprotective Roles of Rabdosia inflexa through Downregulation of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 16;19(2):584. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020584. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29462911 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of mTORC1 signaling protects kidney from irradiation-induced toxicity via accelerating recovery of renal stem-like cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Aug 14;9(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0963-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30107854 Free PMC article.
-
Allylmethylsulfide, a Sulfur Compound Derived from Garlic, Attenuates Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 11;2020:7856318. doi: 10.1155/2020/7856318. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32617142 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Ang II involvement in activation of NF-κB through phosphorylation of p65 during aging.Age (Dordr). 2012 Feb;34(1):11-25. doi: 10.1007/s11357-011-9207-7. Epub 2011 Feb 12. Age (Dordr). 2012. PMID: 21318332 Free PMC article.
-
Allicin Bioavailability and Bioequivalence from Garlic Supplements and Garlic Foods.Nutrients. 2018 Jun 24;10(7):812. doi: 10.3390/nu10070812. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29937536 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Schneider LA, Dissemond J, Brenneisen P, Hainzl A, Briviba K, Wlaschek M, Scharffetter-Kochanek K: Adaptive cellular protection against UVA-1-induced lipid peroxidation in human dermal fibroblasts shows donor-to-donor variability and is glutathione dependent. Arch Dermatol Res 2006;297:324–328 - PubMed
-
- Punnonen K, Puntala A, Jansén CT, Ahotupa M: UVB irradiation induces lipid peroxidation and reduces antioxidant enzyme activities in human keratinocytes in vitro. Acta Derm Venereol 1991;71:239–242 - PubMed
-
- Kharbanda S, Yuan ZM, Rubin E, Weichselbaum R, Kufe D: Activation of Src-like p56/p53lyn tyrosine kinase by ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 1994;269:20739–20743 - PubMed
-
- Mikkelsen RB, Wardman P: Biological chemistry of reactive oxygen and nitrogen and radiation-induced signal transduction mechanisms. Oncogene 2003;22:5734–5754 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

