DAS-28-based EULAR response and HAQ improvement in rheumatoid arthritis patients switching between TNF antagonists
- PMID: 19627609
- PMCID: PMC2724400
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-91
DAS-28-based EULAR response and HAQ improvement in rheumatoid arthritis patients switching between TNF antagonists
Abstract
Introduction: No definitive data are available regarding the value of switching to an alternative TNF antagonist in rheumatoid arthritis patients who fail to respond to the first one. The aim of this study was to evaluate treatment response in a clinical setting based on HAQ improvement and EULAR response criteria in RA patients who were switched to a second or a third TNF antagonist due to failure with the first one.
Methods: This was an observational, prospective study of a cohort of 417 RA patients treated with TNF antagonists in three university hospitals in Spain between January 1999 and December 2005. A database was created at the participating centres, with well-defined operational instructions. The main outcome variables were analyzed using parametric or non-parametric tests depending on the level of measurement and distribution of each variable.
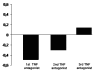
Results: Mean (+/- SD) DAS-28 on starting the first, second and third TNF antagonist was 5.9 (+/- 2.0), 5.1 (+/- 1.5) and 6.1 (+/- 1.1). At the end of follow-up, it decreased to 3.3 (+/- 1.6; Delta = -2.6; p > 0.0001), 4.2 (+/- 1.5; Delta = -1.1; p = 0.0001) and 5.4 (+/- 1.7; Delta = -0.7; p = 0.06). For the first TNF antagonist, DAS-28-based EULAR response level was good in 42% and moderate in 33% of patients. The second TNF antagonist yielded a good response in 20% and no response in 53% of patients, while the third one yielded a good response in 28% and no response in 72%. Mean baseline HAQ on starting the first, second and third TNF antagonist was 1.61, 1.52 and 1.87, respectively. At the end of follow-up, it decreased to 1.12 (Delta = -0.49; p < 0.0001), 1.31 (Delta = -0.21, p = 0.004) and 1.75 (Delta = -0.12; p = 0.1), respectively. Sixty four percent of patients had a clinically important improvement in HAQ (defined as > or = -0.22) with the first TNF antagonist and 46% with the second.
Conclusion: A clinically significant effect size was seen in less than half of RA patients cycling to a second TNF antagonist.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, Keystone EC, Loveless JE, Burmester GR, Cravets MW, Hessey EW, Shaw T, Totoritis MC. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2793–2806. doi: 10.1002/art.22025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, Cantagrel A, van Vollenhoven R, Sanchez A, Alecock E, Lee J, Kremer J. IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1516–23. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.092932. - DOI - PMC - PubMed