Midregional pro-adrenomedullin in addition to b-type natriuretic peptides in the risk stratification of patients with acute dyspnea: an observational study
- PMID: 19627611
- PMCID: PMC2750172
- DOI: 10.1186/cc7975
Midregional pro-adrenomedullin in addition to b-type natriuretic peptides in the risk stratification of patients with acute dyspnea: an observational study
Abstract
Introduction: The identification of patients at highest risk for adverse outcome who are presenting with acute dyspnea to the emergency department remains a challenge. This study investigates the prognostic value of the newly described midregional fragment of the pro-Adrenomedullin molecule (MR-proADM) alone and combined to B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal proBNP (NT-proBNP) in patients with acute dyspnea.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, observational cohort study in the emergency department of a University Hospital and enrolled 287 unselected, consecutive patients (48% women, median age 77 (range 68 to 83) years) with acute dyspnea.
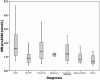
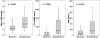
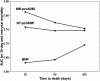
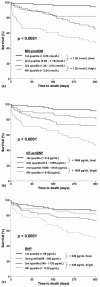
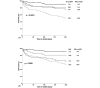
Results: MR-proADM levels were elevated in non-survivors (n = 77) compared to survivors (median 1.9 (1.2 to 3.2) nmol/L vs. 1.1 (0.8 to 1.6) nmol/L; P < 0.001). The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) to predict 30-day mortality were 0.81 (95% CI 0.73 to 0.90), 0.76 (95% CI 0.67 to 0.84) and 0.63 (95% CI 0.53 to 0.74) for MR-proADM, NT-proBNP and BNP, respectively (MRproADM vs. NTproBNP P = 0.38; MRproADM vs. BNP P = 0.009). For one-year mortality the AUC were 0.75 (95% CI 0.69 to 0.81), 0.75 (95% CI 0.68 to 0.81), 0.69 (95% CI 0.62 to 0.76) for MR-proADM, NT-proBNP and BNP, respectively without any significant difference. Using multivariate linear regression analysis, MR-proADM strongly predicted one-year all-cause mortality independently of NT-proBNP and BNP levels (OR = 10.46 (1.36 to 80.50), P = 0.02 and OR = 24.86 (3.87 to 159.80) P = 0.001, respectively). Using quartile approaches, Kaplan-Meier curve analyses demonstrated a stepwise increase in one-year all-cause mortality with increasing plasma levels (P < 0.0001). Combined levels of MR-proADM and NT-proBNP did risk stratify acute dyspneic patients into a low (90% one-year survival rate), intermediate (72 to 82% one-year survival rate) or high risk group (52% one-year survival rate).
Conclusions: MR-proADM alone or combined to NT-proBNP has a potential to assist clinicians in risk stratifying patients presenting with acute dyspnea regardless of the underlying disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Midregional proadrenomedullin (MR-proADM) in the risk stratification of patients with acute pulmonary embolism.Thromb Res. 2013 Nov;132(5):506-10. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Thromb Res. 2013. PMID: 24060192
-
Mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide and pro-adrenomedullin testing for the diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of patients with acute dyspnoea.Eur Heart J. 2012 Sep;33(17):2197-205. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs136. Epub 2012 May 29. Eur Heart J. 2012. PMID: 22645194 Free PMC article.
-
Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in patients with acute dyspnea: Data from the Akershus Cardiac Examination (ACE) 2 Study.Clin Biochem. 2017 May;50(7-8):394-400. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2016.12.010. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Clin Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28065681 Clinical Trial.
-
Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing and prognosis in patients with acute dyspnea, including those with acute heart failure.Am J Cardiol. 2008 Feb 4;101(3A):49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.11.020. Am J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18243859 Review.
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proadm) as a prognostic marker in Covid-19-hospitalized patients.Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):379-387. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2162116. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 36607317 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Plasma concentrations of the vasoactive peptide fragments mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin, C-terminal pro-endothelin 1 and copeptin in hemodialysis patients: associated factors and prediction of mortality.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 22;9(1):e86148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086148. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465926 Free PMC article.
-
Novel biomarkers in acute heart failure.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2011 Sep;8(3):206-11. doi: 10.1007/s11897-011-0065-5. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2011. PMID: 21681444 Review.
-
Tako-Tsubo syndrome: dying of a broken heart?Clin Res Cardiol. 2010 Dec;99(12):771-80. doi: 10.1007/s00392-010-0224-9. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Clin Res Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20848112 Review.
-
Adrenomedullin: a marker of impaired hemodynamics, organ dysfunction, and poor prognosis in cardiogenic shock.Ann Intensive Care. 2017 Dec;7(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13613-016-0229-2. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Ann Intensive Care. 2017. PMID: 28050899 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Procalcitonin (PCT) and Mid regional pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) in risk stratification of critically ill febrile patients in Emergency Department (ED). A comparison with APACHE II score.BMC Infect Dis. 2012 Aug 8;12:184. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-184. BMC Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22874067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu AH, Clopton P, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Perez A, Kazanegra R, Herrmann HC, McCullough PA. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:161–167. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020233. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dyspnea. Mechanisms, assessment, and management: a consensus statement. American Thoracic Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159:321–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

