The advantage of errorless learning for the acquisition of new concepts' labels in alcoholics
- PMID: 19627642
- PMCID: PMC3021538
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291709990626
The advantage of errorless learning for the acquisition of new concepts' labels in alcoholics
Abstract
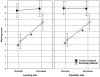
Background: Previous findings revealed that the acquisition of new semantic concepts' labels was impaired in uncomplicated alcoholic patients. The use of errorless learning may therefore allow them to improve learning performance. However, the flexibility of the new knowledge and the memory processes involved in errorless learning remain unclear.
Method: New concepts' labels acquisition was examined in 15 alcoholic patients and 15 control participants in an errorless learning condition compared with 19 alcoholic patients and 19 control subjects in a trial-and-error learning condition. The flexibility of the new information was evaluated using different photographs from those used in the learning sessions but representing the same concepts. All of the participants carried out an additional explicit memory task and an implicit memory task was also performed by subjects in the errorless learning condition.
Results: The alcoholic group in the errorless condition differed significantly from the alcoholic group in the trial-and-error condition but did not differ from the two control groups. There was no significant difference between results in the learning test and the flexibility task. Finally, in the alcoholic group, the naming score in the learning test was correlated with the explicit memory score but not with the implicit memory score.
Conclusions: Using errorless learning, alcoholics improved their abilities to learn new concepts' labels. Moreover, new knowledge acquired with errorless learning was flexible. The errorless learning advantage may rely on explicit rather than implicit memory processes in these alcohol-dependent patients presenting only mild to moderate deficits of explicit memory capacities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An investigation of errorless learning in memory-impaired patients: improving the technique and clarifying theory.Neuropsychologia. 2003;41(9):1230-40. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3932(03)00036-8. Neuropsychologia. 2003. PMID: 12753962
-
The mnemonic mechanisms of errorless learning.Neuropsychologia. 2006;44(14):2806-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.05.026. Epub 2006 Aug 9. Neuropsychologia. 2006. PMID: 16901519
-
Perceptual learning in detoxified alcoholic men: contributions from explicit memory, executive function, and age.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004 Nov;28(11):1657-65. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000145690.48510.da. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004. PMID: 15547452
-
Errorless learning in cognitive rehabilitation: a critical review.Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2012;22(2):138-68. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2011.639619. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2012. PMID: 22247957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does implicit motor learning lead to greater automatization of motor skills compared to explicit motor learning? A systematic review.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 5;13(9):e0203591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203591. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30183763 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neural correlates of the severity of cocaine, heroin, alcohol, MDMA and cannabis use in polysubstance abusers: a resting-PET brain metabolism study.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039830. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768136 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of intermediate-term alcohol abstinence on memory retrieval and suppression.Front Psychol. 2014 Dec 2;5:1396. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01396. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2014. PMID: 25520692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical manual of Mental Disorders. 4. Washington: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Anderson ND, Craik FI. The mnemonic mechanisms of errorless learning. Neuropsychologia. 2006;44:2806–2813. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley A, Wilson BA. When implicit learning fails: amnesia and the problem of error elimination. Neuropsychologia. 1994;32:53–68. - PubMed
-
- Chambaron S, Ginhac D, Perruchet P. gSRT-Soft: A generic software and some methodological guidelines to investigate implicit learning through visual-motor sequential tasks. Behavior Research Methods. 2008;40:493–502. - PubMed
-
- Clare L, Jones SP. Errorless learning in the rehabilitation of memory impairment: a critical review. Neuropsychology Review. 2008;18:1–23. - PubMed

