Transcription of the C. elegans let-7 microRNA is temporally regulated by one of its targets, hbl-1
- PMID: 19627983
- PMCID: PMC2753757
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.07.012
Transcription of the C. elegans let-7 microRNA is temporally regulated by one of its targets, hbl-1
Abstract
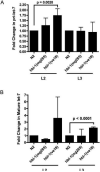
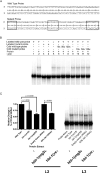
The let-7 family of microRNAs (miRNAs) are important regulators of developmental timing and cell differentiation and are often misexpressed in human cancer. In C. elegans, let-7 controls cell fate transitions from larval stage 4 (L4) to adulthood by post-transcriptionally down-regulating lineage-abnormal 41 (lin-41) and hunchback-like 1 (hbl-1). Primary let-7 (pri-let-7) transcripts are up-regulated in the L3, yet little is known about what controls this transcriptional up-regulation. We sought factors that either turn on let-7 transcription or keep it repressed until the correct time. Here we report that one of let-7's targets, the transcription factor Hunchback-like 1 (HBL-1), is responsible for inhibiting the transcription of let-7 in specific tissues until the L3. hbl-1 is a known developmental timing regulator and inhibits adult development in larval stages. Therefore, one important function of HBL-1 in maintaining larval stage fates is inhibition of let-7. Indeed, our results reveal let-7 as the first known target of the HBL-1 transcription factor in C. elegans and suggest a negative feedback loop mechanism for let-7 and HBL-1 regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs.Dev Cell. 2003 May;4(5):625-37. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00127-8. Dev Cell. 2003. PMID: 12737799
-
The C elegans hunchback homolog, hbl-1, controls temporal patterning and is a probable microRNA target.Dev Cell. 2003 May;4(5):639-50. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00124-2. Dev Cell. 2003. PMID: 12737800
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans pumilio homolog, puf-9, is required for the 3'UTR-mediated repression of the let-7 microRNA target gene, hbl-1.Dev Biol. 2007 May 15;305(2):551-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.02.040. Epub 2007 Mar 3. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17412319 Free PMC article.
-
Heterochronic genes and the nature of developmental time.Curr Biol. 2007 Jun 5;17(11):R425-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.03.043. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17550772 Review.
-
An elegant miRror: microRNAs in stem cells, developmental timing and cancer.Chromosoma. 2009 Aug;118(4):405-18. doi: 10.1007/s00412-009-0210-z. Epub 2009 Apr 3. Chromosoma. 2009. PMID: 19340450 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple cis-elements and trans-acting factors regulate dynamic spatio-temporal transcription of let-7 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Dev Biol. 2013 Feb 1;374(1):223-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.11.021. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23201578 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Profiling of Caenorhabditis elegans Starvation-Responsive microRNAs.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 10;10(11):e0142262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142262. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26554708 Free PMC article.
-
Diet-regulated transcriptional plasticity of plant parasites in plant-mutualist environments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Apr 22;122(16):e2421367122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2421367122. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40244681 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of gene expression in C. elegans.WormBook. 2013 Jun 4:1-34. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.45.2. WormBook. 2013. PMID: 23801596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of microRNA expression and function.Methods Cell Biol. 2011;106:219-252. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-544172-8.00008-6. Methods Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22118279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrahante JE, Daul AL, Li M, Volk ML, Tennessen JM, Miller EA, Rougvie AE. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev Cell. 2003;4:625–37. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. A hierarchy of regulatory genes controls a larva-to-adult developmental switch in C. elegans. Cell. 1989;57:49–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

