MeCP2 deficiency disrupts axonal guidance, fasciculation, and targeting by altering Semaphorin 3F function
- PMID: 19628041
- PMCID: PMC3290450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2009.07.009
MeCP2 deficiency disrupts axonal guidance, fasciculation, and targeting by altering Semaphorin 3F function
Abstract
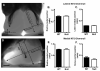
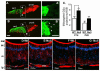
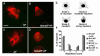
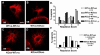
Rett syndrome (RTT) is an autism spectrum disorder that results from mutations in the transcriptional regulator methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MECP2). In the present work, we demonstrate that MeCP2 deficiency disrupts the establishment of neural connections before synaptogenesis. Using both in vitro and in vivo approaches, we identify dynamic alterations in the expression of class 3 semaphorins that are accompanied by defects in axonal fasciculation, guidance, and targeting with MeCP2 deficiency. Olfactory axons from Mecp2 mutant mice display aberrant repulsion when co-cultured with mutant olfactory bulb explants. This defect is restored when mutant olfactory axons are co-cultured with wild type olfactory bulbs. Thus, a non-cell autonomous mechanism involving Semaphorin 3F function may underlie abnormalities in the establishment of connectivity with Mecp2 mutation. These findings have broad implications for the role of MECP2 in neurodevelopment and RTT, given the critical role of the semaphorins in the formation of neural circuits.
Figures





References
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DD. Rett syndrome neuropathology review 2000. Brain Dev. 2001;23(Suppl 1):S72–76. - PubMed
-
- Asaka Y, Jugloff DG, Zhang L, Eubanks JH, Fitzsimonds RM. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity is impaired in the Mecp2-null mouse model of Rett syndrome. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;21:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Belichenko NP, Belichenko PV, Mobley WC. Evidence for both neuronal cell autonomous and nonautonomous effects of methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 in the cerebral cortex of female mice with Mecp2 mutation. Neurobiol Dis. 2009a;34:71–77. - PubMed
-
- Belichenko PV, Wright EE, Belichenko NP, Masliah E, Li HH, Mobley WC, Francke U. Widespread changes in dendritic and axonal morphology in Mecp2-mutant mouse models of Rett syndrome: evidence for disruption of neuronal networks. J Comp Neurol. 2009b;514:240–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

