Relationship of hemoglobin A1C and mortality in heart failure patients with diabetes
- PMID: 19628117
- PMCID: PMC2753214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.049
Relationship of hemoglobin A1C and mortality in heart failure patients with diabetes
Abstract
Objectives: This study was designed to examine the relationship between glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) and adverse outcomes in diabetic patients with established heart failure (HF).
Background: Despite the common coexistence of diabetes and HF, previous studies examining the association between HbA1C and outcomes in this population have been limited and have reported discrepant results.
Methods: We assessed the association between increasing quintiles (Q1 to Q5) of HbA1C and risk of death or risk of HF hospitalization by conducting a retrospective study in a national cohort of 5,815 veterans with HF and diabetes treated in ambulatory clinics at Veterans Affairs medical centers.
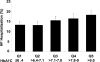
Results: At 2 years of follow-up, death occurred in 25% of patients in Q1 (HbA1C < or =6.4%), 23% in Q2 (6.4% < HbA1c < or =7.1%), 17.7% in Q3 (7.1% < HbA1c < or =7.8%), 22.5% in Q4 (7.8% < HbA1c < or =9.0%), and 23.2% in Q5 (HbA1c >9.0%). After adjustment for potential confounders, the middle quintile (Q3) had reduced mortality when compared with the lowest quintile (risk-adjusted hazard ratio: 0.73, 95% confidence interval: 0.61 to 0.88, p = 0.001). Hospitalization rates for HF at 2 years increased with increasing quintiles of HbA1C (Q1: 13.3%, Q2: 13.1%, Q3: 15.5%, Q4: 16.4%, and Q5: 18.2%), but this association was not statistically significant when adjusted for potential confounders.
Conclusions: The association between mortality and HbA1C in diabetic patients with HF appears U-shaped, with the lowest risk of death in those patients with modest glucose control (7.1% < HbA1C < or =7.8%). Future prospective studies are necessary to define optimal treatment goals in these patients.
Figures
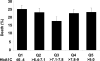
Comment in
-
Aiming for the best control of glycemia in patients with heart failure and type 2 diabetes the "sweet spot".J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 Jul 28;54(5):429-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.05.014. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19628118 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Association Between Type 2 Diabetes and All-Cause Hospitalization and Mortality in the UK General Heart Failure Population: Stratification by Diabetic Glycemic Control and Medication Intensification.JACC Heart Fail. 2018 Jan;6(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2017.08.020. Epub 2017 Oct 11. JACC Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29032131
-
Relation between hemoglobin a(1c) and outcomes in heart failure patients with and without diabetes mellitus.Am J Cardiol. 2012 Jun 15;109(12):1767-73. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.02.022. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Am J Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22459300 Free PMC article.
-
Mean HbA1c and mortality in diabetic individuals with heart failure: a population cohort study.Eur J Heart Fail. 2016 Jan;18(1):94-102. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.455. Epub 2015 Dec 13. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016. PMID: 26663216
-
Glycated Hemoglobin and Outcomes of Heart Failure (from Get With the Guidelines-Heart Failure).Am J Cardiol. 2019 Feb 15;123(4):618-626. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.11.023. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30553509
-
Hemoglobin A1c predicts heart failure hospitalization independent of baseline cardiac function or B-type natriuretic peptide level.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014 May;104(2):257-65. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 24629410
Cited by
-
Use of the biomarker score in determining the risk of heart failure in diabetics in Goma, North Kivu in the Democractic Republic of the Congo.Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024 Mar 30;21:200263. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcrp.2024.200263. eCollection 2024 Jun. Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024. PMID: 39118986 Free PMC article.
-
After avandia: the use of antidiabetic drugs in patients with heart failure.Tex Heart Inst J. 2012;39(2):174-8. Tex Heart Inst J. 2012. PMID: 22740727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addressing Comorbidities in Heart Failure: Hypertension, Atrial Fibrillation, and Diabetes.Heart Fail Clin. 2020 Oct;16(4):441-456. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2020.06.005. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Heart Fail Clin. 2020. PMID: 32888639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin sensitizers and heart failure: an engine flooded with fuel.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2010 Dec;12(6):399-401. doi: 10.1007/s11906-010-0158-7. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2010. PMID: 20963518 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiogenic diabetes.Heart Fail Rev. 2014 Sep;19(5):595-602. doi: 10.1007/s10741-013-9412-9. Heart Fail Rev. 2014. PMID: 24174218 Review.
References
-
- Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, et al. ACC/AHA 2005 Guideline Update for the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Heart Failure in the Adult: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Update the 2001 Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Heart Failure): developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians and the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2005;112:e154–235. - PubMed
-
- Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA. 2003;289:76–9. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes mellitus: a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. A joint editorial statement by the American Diabetes Association; The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; The Juvenile Diabetes Foundation International; The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; and The American Heart Association. Circulation. 1999;100:1132–3. - PubMed
-
- Gottdiener JS, Arnold AM, Aurigemma GP, et al. Predictors of congestive heart failure in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:1628–37. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA. 1979;241:2035–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

