Closure of schools during an influenza pandemic
- PMID: 19628172
- PMCID: PMC7106429
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70176-8
Closure of schools during an influenza pandemic
Abstract
In response to WHO raising the influenza pandemic alert level from phase five to phase six, health officials around the world are carefully reviewing pandemic mitigation protocols. School closure (also called class dismissal in North America) is a non-pharmaceutical intervention that is commonly suggested for mitigating influenza pandemics. Health officials taking the decision to close schools must weigh the potential health benefits of reducing transmission and thus case numbers against high economic and social costs, difficult ethical issues, and the possible disruption of key services such as health care. Also, if schools are expected to close as a deliberate policy option, or just because of high levels of staff absenteeism, it is important to plan to mitigate the negative features of closure. In this context, there is still debate about if, when, and how school closure policy should be used. In this Review, we take a multidisciplinary and holistic perspective and review the multiple aspects of school closure as a public health policy. Implications for the mitigation of the swine-origin influenza A H1N1 pandemic are also discussed.
Figures
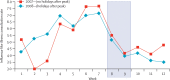

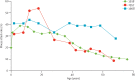
Comment in
-
Pandemic influenza on Reunion Island and school closure.Lancet Infect Dis. 2010 May;10(5):294-5. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70076-1. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20417411 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO . Influenza A(H1N1)—update 42. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2009. http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_06_01a/en/index.html (accessed June 29, 2009).
-
- Chan M. World now at the start of 2009 influenza pandemic. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2009. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/statements/2009/h1n1_pandemic_phase6... (accessed June 29, 2009).
-
- WHO . WHO global influenza preparedness plan: the role of WHO and recommendations for national measures before and during pandemics. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2005. http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/influenza/WHO_CDS_CSR_GIP_... (accessed June 29, 2009).
-
- Novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus investigation team Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2605–2615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

