Extracellular nucleotides as negative modulators of immunity
- PMID: 19628431
- PMCID: PMC4158611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.06.021
Extracellular nucleotides as negative modulators of immunity
Abstract
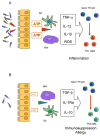
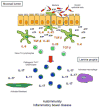
Nucleotides are well known for being the universal currency of intracellular energy transactions, but over the past decade it has become clear that they are also ubiquitous extracellular messengers. In the immune system there is increasing awareness that nucleotides serve multiple roles as stimulants of lymphocyte proliferation, ROS generation, cytokine and chemokine secretion: in one word as pro-inflammatory mediators. However, although often neglected, extracellular nucleotides exert an additional more subtle function as negative modulators of immunity, or as immunodepressants. The more we understand the peculiar biochemical composition of the microenvironment generated at inflammatory sites, the more we appreciate how chronic exposure to low extracellular nucleotide levels affect immunity and inflammation. A deeper understanding of this complex network will no doubt help design more effective therapies for cancer and chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Burnstock G. The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signalling molecules. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1127–1139. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Pathophysiology and therapeutic potential of purinergic signaling. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:58–86. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:659–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

