Genetic enhancement of calcitonin gene-related Peptide-induced central sensitization to mechanical stimuli in mice
- PMID: 19628434
- PMCID: PMC2752439
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.03.018
Genetic enhancement of calcitonin gene-related Peptide-induced central sensitization to mechanical stimuli in mice
Abstract
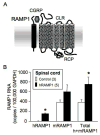
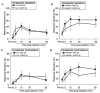
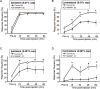
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a key player in migraine. To address the role of CGRP in mechanical allodynia, which is a common feature of migraine, we used CGRP-sensitized transgenic mice. These mice have elevated nervous-system expression of the human receptor activity-modifying protein-1 (hRAMP1) subunit of the CGRP receptor. Under baseline conditions, the nestin/hRAMP1 mice and control littermates had similar hindpaw withdrawal thresholds to von Frey filaments. The effect of CGRP was tested using a filament that elicited a withdrawal response on 20% of its presentations. Following intrathecal injection of 1 nmol CGRP in the nestin/hRAMP1 mice, the response frequency was 80% within 30 minutes. The antagonist CGRP(8-37) blocked the increased response. In control littermates, a 5-fold higher dose of CGRP was required to elicit a similar response. In contrast to intrathecal injection, peripheral CGRP did not increase the mechanical responses. Intraplantar injection of capsaicin was used to test the efficacy of endogenous CGRP. Capsaicin increased mechanical responses in the nestin/hRAMP1 and control mice, although a higher dose was required in controls. In contrast to control mice, there was also a contralateral paw response in nestin/hRAMP1 mice, which is consistent with central sensitization.
Perspective: In this study we show central CGRP-induced mechanical allodynia that is enhanced by overexpression of RAMP1 in nervous system. These data suggest that hypersensitivity to CGRP could be a potential mechanism underlying central sensitization in migraine and point to CGRP-receptor antagonists as a possible therapy for other pain disorders.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Induction of multiple photophobic behaviors in a transgenic mouse sensitized to CGRP.Neuropharmacology. 2010 Jan;58(1):156-65. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.07.009. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Neuropharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19607849 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitization of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors by receptor activity-modifying protein-1 in the trigeminal ganglion.J Neurosci. 2007 Mar 7;27(10):2693-703. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4542-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17344407 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of dorsal horn CGRP-expressing interneurons to mechanical sensitivity.Elife. 2021 Jun 1;10:e59751. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59751. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34061020 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Migraine-Like Photophobic Behavior in Mice by Both Peripheral and Central CGRP Mechanisms.J Neurosci. 2017 Jan 4;37(1):204-216. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2967-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28053042 Free PMC article.
-
The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine.Pain. 2017 Apr;158(4):543-559. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000831. Pain. 2017. PMID: 28301400 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vascular Contributions to Migraine: Time to Revisit?Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Aug 3;12:233. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00233. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30127722 Free PMC article.
-
Human RAMP1 overexpressing mice are resistant to migraine therapies for motion sensitivity.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 9;19(12):e0313482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313482. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39652533 Free PMC article.
-
Migraine in the era of precision medicine.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Mar;4(6):105. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.03.13. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27127758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CGRP receptor activity in mice with global expression of human receptor activity modifying protein 1.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Jun;174(12):1826-1840. doi: 10.1111/bph.13783. Epub 2017 Apr 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28317098 Free PMC article.
-
An underrepresented majority: A systematic review utilizing allodynic criteria to examine the present scarcity of discrete animal models for episodic migraine.Cephalalgia. 2021 Mar;41(3):404-416. doi: 10.1177/0333102420966984. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Cephalalgia. 2021. PMID: 33131303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen GV, Barbrick B, Esser MJ. Trigeminal-parabrachial connections: possible pathway for nociception-induced cardiovascular reflex responses. Brain Res. 1996;715:125–135. - PubMed
-
- Ashina M, Bendtsen L, Jensen R, Schifter S, Olesen J. Evidence for increased plasma levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide in migraine outside of attacks. Pain. 2000;86:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Bennett AD, Chastain KM, Hulsebosch CE. Alleviation of mechanical and thermal allodynia by CGRP(8-37) in a rodent model of chronic central pain. Pain. 2000;86:163–175. - PubMed
-
- Bereiter DA, Benetti AP. Microinjections of calcitonin gene-related peptide within the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis of the cat affects adrenal and autonomic function. Brain Res. 1991;558:53–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

