Cyclin D2 protein stability is regulated in pancreatic beta-cells
- PMID: 19628581
- PMCID: PMC2775938
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0057
Cyclin D2 protein stability is regulated in pancreatic beta-cells
Abstract
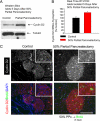
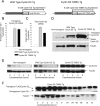
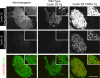
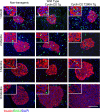
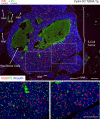
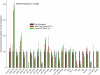
The molecular determinants of beta-cell mass expansion remain poorly understood. Cyclin D2 is the major D-type cyclin expressed in beta-cells, essential for adult beta-cell growth. We hypothesized that cyclin D2 could be actively regulated in beta-cells, which could allow mitogenic stimuli to influence beta-cell expansion. Cyclin D2 protein was sharply increased after partial pancreatectomy, but cyclin D2 mRNA was unchanged, suggesting posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms influence cyclin D2 expression in beta-cells. Consistent with this hypothesis, cyclin D2 protein stability is powerfully regulated in fibroblasts. Threonine 280 of cyclin D2 is phosphorylated, and this residue critically limits D2 stability. We derived transgenic (tg) mice with threonine 280 of cyclin D2 mutated to alanine (T280A) or wild-type cyclin D2 under the control of the insulin promoter. Cyclin D2 T280A protein was expressed at much higher levels than wild-type cyclin D2 protein in beta-cells, despite equivalent expression of tg mRNAs. Cyclin D2 T280A tg mice exhibited a constitutively nuclear cyclin D2 localization in beta-cells, and increased cyclin D2 stability in islets. Interestingly, threonine 280-mutant cyclin D2 tg mice had greatly reduced beta-cell apoptosis, with suppressed expression of proapoptotic genes. Suppressed beta-cell apoptosis in threonine 280-mutant cyclin D2 tg mice resulted in greatly increased beta-cell area in aged mice. Taken together, these data indicate that cyclin D2 is regulated by protein stability in pancreatic beta-cells, that signals that act upon threonine 280 limit cyclin D2 stability in beta-cells, and that threonine 280-mutant cyclin D2 overexpression prolongs beta-cell survival and augments beta-cell mass expansion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
mTORC1 pathway mediates beta cell compensatory proliferation in 60 % partial-pancreatectomy mice.Endocrine. 2016 Jul;53(1):117-28. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0861-5. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Endocrine. 2016. PMID: 26818915
-
PKCζ Is Essential for Pancreatic β-Cell Replication During Insulin Resistance by Regulating mTOR and Cyclin-D2.Diabetes. 2016 May;65(5):1283-96. doi: 10.2337/db15-1398. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 26868297 Free PMC article.
-
Akt induces beta-cell proliferation by regulating cyclin D1, cyclin D2, and p21 levels and cyclin-dependent kinase-4 activity.Diabetes. 2006 Feb;55(2):318-25. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-0757. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 16443763
-
Glucose regulates cyclin D2 expression in quiescent and replicating pancreatic β-cells through glycolysis and calcium channels.Endocrinology. 2011 Jul;152(7):2589-98. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-1372. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21521747 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of type 2 diabetes with reduced pancreatic beta-cell mass.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(5-6):873-93. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.09.007. Epub 2005 Oct 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16253543 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral cyclins mediate separate phases of infection by integrating functions of distinct mammalian cyclins.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Feb;8(2):e1002496. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002496. Epub 2012 Feb 2. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22319441 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of protein kinase C-ζ in pancreatic β-cells in vivo improves glucose tolerance and induces β-cell expansion via mTOR activation.Diabetes. 2011 Oct;60(10):2546-59. doi: 10.2337/db10-1783. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21911744 Free PMC article.
-
Incretin Therapies Do Not Expand β-Cell Mass or Alter Pancreatic Histology in Young Male Mice.Endocrinology. 2017 Jun 1;158(6):1701-1714. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-00027. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28323942 Free PMC article.
-
Transient overexpression of cyclin D2/CDK4/GLP1 genes induces proliferation and differentiation of adult pancreatic progenitors and mediates islet regeneration.Cell Cycle. 2012 Feb 15;11(4):695-705. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.4.19120. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22373529 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 signalling compensates for impaired insulin signalling in regulating beta cell proliferation in βIRKO mice.Diabetologia. 2017 Aug;60(8):1442-1453. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4303-6. Epub 2017 May 20. Diabetologia. 2017. PMID: 28526921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherr CJ 2000 The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res 60:3689–3695 - PubMed
-
- Rane SG, Dubus P, Mettus RV, Galbreath EJ, Boden G, Reddy EP, Barbacid M 1999 Loss of cdk4 expression causes insulin-deficient diabetes and cdk4 activation results in β-islet cell hyperplasia. Nat Genet 22:44–52 - PubMed
-
- Malumbres M, Sotillo R, Santamaría D, Galán J, Cerezo A, Ortega S, Dubus P, Barbacid M 2004 Mammalian cells cycle without the D-type cyclin-dependent kinases Cdk4 and Cdk6. Cell 118:493–504 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

