A preformed signaling complex mediates GnRH-activated ERK phosphorylation of paxillin and FAK at focal adhesions in L beta T2 gonadotrope cells
- PMID: 19628583
- PMCID: PMC5419161
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0260
A preformed signaling complex mediates GnRH-activated ERK phosphorylation of paxillin and FAK at focal adhesions in L beta T2 gonadotrope cells
Abstract
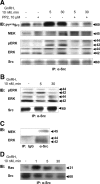
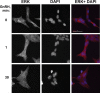
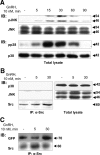
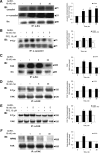
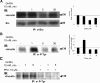
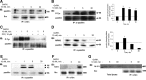
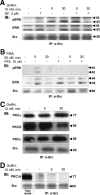
Most receptor tyrosine kinases and G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) operate via a limited number of MAPK cascades but still exert diverse functions, and therefore signal specificity remains an enigma. Also, most GPCR ligands utilize families of receptors for mediation of diverse biological actions; however, the mammalian type I GnRH receptor (GnRHR) seems to be the sole receptor mediating GnRH-induced gonadotropin synthesis and release. Signaling complexes associated with GPCRs may thus provide the means for signal specificity. Here we describe a signaling complex associated with the GnRHR, which is a unique GPCR lacking a C-terminal tail. Unlike other GPCRs, this signaling complex is preformed, and exposure of L beta T2 gonadotropes to GnRH induces its dynamic rearrangement. The signaling complex includes c-Src, protein kinase C delta, -epsilon, and -alpha, Ras, MAPK kinase 1/2, ERK1/2, tubulin, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), paxillin, vinculin, caveolin-1, kinase suppressor of Ras-1, and the GnRHR. Exposure to GnRH (5 min) causes MAPK kinase 1/2, ERK1/2, tubulin, vinculin, and the GnRHR to detach from c-Src, but they reassociate within 30 min. On the other hand, FAK, paxillin, the protein kinase Cs, and caveolin-1 stay bound to c-Src, whereas kinase suppressor of Ras-1 appears in the complex only 30 min after GnRH stimulation. GnRH was found to activate ERK1/2 in the complex in a c-Src-dependent manner, and the activated ERK1/2 subsequently phosphorylates FAK and paxillin. In parallel, caveolin-1, FAK, vinculin, and paxillin are phosphorylated on Tyr residues apparently by GnRH-activated c-Src. Receptor tyrosine kinases and GPCRs translocate ERK1/2 to the nucleus to phosphorylate and activate transcription factors. We therefore propose that the role of the multiprotein signaling complex is to sequester a cytosolic pool of activated ERK1/2 to phosphorylate FAK and paxillin at focal adhesions.
Figures


References
-
- Naor Z1990. Signal transduction mechanisms of Ca2+ mobilizing hormones: the case of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Endocr Rev 11:326–353 - PubMed
-
- Sealfon SC, Weinstein H, Millar RP1997. Molecular mechanisms of ligand interaction with the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor. Endocr Rev 18:180–205 - PubMed
-
- Shacham S, Harris D, Ben-Shlomo H, Cohen I, Bonfil D, Przedecki F, Lewy H, Ashkenazi IE, Seger R, Naor Z2001. Mechanism of GnRH receptor signaling on gonadotropin release and gene expression in pituitary gonadotrophs. Vitam Horm 63:63–90 - PubMed
-
- Millar RP, Lu ZL, Pawson AJ, Flanagan CA, Morgan K, Maudsley SR2004. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors. Endocr Rev 25:235–275 - PubMed
-
- Dobkin-Bekman M, Naidich M, Pawson AJ, Millar RP, Seger R, Naor Z2006. Activation of Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) by GnRH is cell-context dependent. Mol Cell Endocrinol 252:184–190 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

