Evaluation of the occlusion status of coiled intracranial aneurysms with MR angiography at 3T: is contrast enhancement necessary?
- PMID: 19628623
- PMCID: PMC7051484
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1678
Evaluation of the occlusion status of coiled intracranial aneurysms with MR angiography at 3T: is contrast enhancement necessary?
Abstract
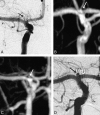
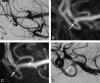
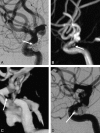
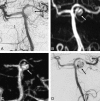
Background and purpose: MR angiography (MRA) is increasingly used as a noninvasive imaging technique for the follow-up of coiled intracranial aneurysms. However, the need for contrast enhancement has not yet been elucidated. We compared 3D time-of-flight MRA (TOF-MRA) and contrast-enhanced MRA (CE-MRA) at 3T with catheter angiography.
Materials and methods: Sixty-seven patients with 72 aneurysms underwent TOF-MRA, CE-MRA, and catheter-angiography 6 months after coiling. Occlusion status on MRA was classified as adequate (complete and neck remnant) or incomplete by 2 independent observers. For TOF-MRA and CE-MRA, interobserver agreement, intermodality agreement, and correlation with angiography were assessed by kappa statistics.
Results: Catheter-angiography revealed incomplete occlusion in 12 (17%) of the 69 aneurysms; 3 aneurysms were excluded due to MR imaging artifacts. Interobserver agreement was good for CE-MRA (kappa = 0.77; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55-0.98) and very good for TOF-MRA (kappa = 0.89; 95% CI, 0.75-1.00). Correlation of TOF-MRA and CE-MRA with angiography was good. The sensitivity of TOF-MRA and CE-MRA was 75% (95% CI, 43%-95%); the specificity of TOF-MRA was 98% (95% CI, 91%-100%) and of CE-MRA, 97% (95% CI, 88%-100%). All 5 incompletely occluded aneurysms, which were additionally treated, were correctly identified with both MRA techniques. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve for TOF-MRA and CE-MRA were 0.90 (95% CI, 0.79-1.00) and 0.91 (95% CI, 0.79-1.00). Intermodality agreement between TOF-MRA and CE-MRA was very good (kappa = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.65-1.00), with full agreement in 66 (96%) of the 69 aneurysms.
Conclusions: In this study, TOF-MRA and CE-MRA at 3T were equivalent in evaluating the occlusion status of intracranial aneurysms after coiling. Because TOF-MRA does not involve contrast administration, this method is preferred over CE-MRA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contrast-Enhanced and Time-of-Flight MR Angiographic Assessment of Endovascular Coiled Intracranial Aneurysms at 1.5 T.Interv Neuroradiol. 2014 Dec;20(6):686-92. doi: 10.15274/INR-2014-10064. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Interv Neuroradiol. 2014. PMID: 25496678 Free PMC article.
-
Follow-up of coiled cerebral aneurysms at 3T: comparison of 3D time-of-flight MR angiography and contrast-enhanced MR angiography.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Sep;29(8):1530-6. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1166. Epub 2008 Jun 12. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. PMID: 18556359 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Usefulness of contrast-enhanced and TOF MR angiography for follow-up after low-profile stent-assisted coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms.Interv Neuroradiol. 2018 Dec;24(6):655-661. doi: 10.1177/1591019918785910. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Interv Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 29976108 Free PMC article.
-
MRA versus DSA for the follow-up imaging of intracranial aneurysms treated using endovascular techniques: a meta-analysis.J Neurointerv Surg. 2019 Oct;11(10):1009-1014. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-014936. Epub 2019 May 2. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019. PMID: 31048457 Review.
-
MR Angiography: Contrast-Enhanced Acquisition Techniques.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2023 Aug;31(3):493-501. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2023.04.007. Epub 2023 Jun 3. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2023. PMID: 37414474 Review.
Cited by
-
Follow-Up Assessment of Intracranial Aneurysms Treated with Endovascular Coiling: Comparison of Compressed Sensing and Parallel Imaging Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography.Tomography. 2022 Jun 18;8(3):1608-1617. doi: 10.3390/tomography8030133. Tomography. 2022. PMID: 35736881 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of remnant size in embolized intracranial aneurysms measured at follow-up with DSA and MRA.Neuroradiology. 2012 Dec;54(12):1381-8. doi: 10.1007/s00234-012-1063-3. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Neuroradiology. 2012. PMID: 22790180 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Imaging Follow-Up of Patients with Coiled Basilar Tip Aneurysms Up to 20 Years.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015 Nov;36(11):2108-13. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4410. Epub 2015 Jul 16. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 26185324 Free PMC article.
-
Mid-term 3T MRA follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with the Woven EndoBridge.Interv Neuroradiol. 2018 Dec;24(6):601-607. doi: 10.1177/1591019918788346. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Interv Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 30001648 Free PMC article.
-
Getting More Out of Follow-up Three-Dimensional Time-of-Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography in Endovascularly Treated Intracranial Aneurysms.Asian J Neurosurg. 2020 Dec 21;15(4):889-898. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_374_20. eCollection 2020 Oct-Dec. Asian J Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 33708659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, et al. , for the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 2002;360:1267 - PubMed
-
- Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Rinkel GJ, et al. Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with detachable coils: long-term clinical and serial angiography results. Radiology 2003;227:720–24 - PubMed
-
- Cognard C, Weill A, Spelle L, et al. Long-term angiographic follow-up of 169 intracranial aneurysms occluded with detachable coils. Radiology 1999;212:348–56 - PubMed
-
- Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, et al. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke 2003;34:1398–403 - PubMed
-
- Piotin M, Spelle L, Mounayer C, et al. Intracranial aneurysms: treatment with bare platinum coils—aneurysm packing, complex coils, and angiographic recurrence. Radiology 2007;243:500–08 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
