Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes podocyte dysfunction and albuminuria
- PMID: 19628668
- PMCID: PMC2736766
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2009010019
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes podocyte dysfunction and albuminuria
Abstract
Podocyte dysfunction, one of the major causes of proteinuria, leads to glomerulosclerosis and end stage renal disease, but its underlying mechanism remains poorly understood. Here we show that Wnt/beta-catenin signaling plays a critical role in podocyte injury and proteinuria. Treatment with adriamycin induced Wnt and activated beta-catenin in mouse podocytes. Overexpression of Wnt1 in vivo activated glomerular beta-catenin and aggravated albuminuria and adriamycin-induced suppression of nephrin expression, whereas blockade of Wnt signaling with Dickkopf-1 ameliorated podocyte lesions. Podocyte-specific knockout of beta-catenin protected against development of albuminuria after injury. Moreover, pharmacologic activation of beta-catenin induced albuminuria in wild-type mice but not in beta-catenin-knockout littermates. In human proteinuric kidney diseases such as diabetic nephropathy and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, we observed upregulation of Wnt1 and active beta-catenin in podocytes. Ectopic expression of either Wnt1 or stabilized beta-catenin in vitro induced the transcription factor Snail and suppressed nephrin expression, leading to podocyte dysfunction. These results suggest that targeting hyperactive Wnt/beta-catenin signaling may represent a novel therapeutic strategy for proteinuric kidney diseases.
Figures



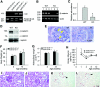
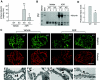
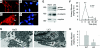
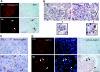
Comment in
-
Activation of canonical Wnt signaling meets with podocytopathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Sep;20(9):1864-6. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009070762. Epub 2009 Aug 27. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19713303 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Levey AS:Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298: 2038–2047, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Eknoyan G, Lameire N, Barsoum R, Eckardt KU, Levin A, Levin N, Locatelli F, MacLeod A, Vanholder R, Walker R, Wang H:The burden of kidney disease: Improving global outcomes. Kidney Int 66: 1310–1314, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Wiggins RC:The spectrum of podocytopathies: A unifying view of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int 71: 1205–1214, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Shankland SJ:The podocyte's response to injury: Role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 69: 2131–2147, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Kim JM, Wu H, Green G, Winkler CA, Kopp JB, Miner JH, Unanue ER, Shaw AS:CD2-associated protein haploinsufficiency is linked to glomerular disease susceptibility. Science 300: 1298–1300, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

