Optimized Gal4 genetics for permanent gene expression mapping in zebrafish
- PMID: 19628697
- PMCID: PMC2726396
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0903060106
Optimized Gal4 genetics for permanent gene expression mapping in zebrafish
Abstract
Combinatorial genetics for conditional transgene activation allows studying gene function with temporal and tissue specific control like the Gal4-UAS system, which has enabled sophisticated genetic studies in Drosophila. Recently this system was adapted for zebrafish and promising applications have been introduced. Here, we report a systematic optimization of zebrafish Gal4-UAS genetics by establishing an optimized Gal4-activator (KalTA4). We provide quantitative data for KalTA4-mediated transgene activation in dependence of UAS copy numbers to allow for studying dosage effects of transgene expression. Employing a Tol2 transposon-mediated KalTA4 enhancer trap screen biased for central nervous system expression, we present a collection of self-reporting red fluorescent KalTA4 activator strains. These strains reliably transactivate UAS-dependent transgenes and can be rendered homozygous. Furthermore, we have characterized the transactivation kinetics of tissue-specific KalTA4 activation, which led to the development of a self-maintaining effector strain "Kaloop." This strain relates transient KalTA4 expression during embryogenesis via a KalTA4-mediated autoregulatory mechanism to live adult structures. We demonstrate its use by showing that the secondary octaval nucleus in the adult hindbrain is likely derived from egr2b-expressing cells in rhombomere 5 during stages of early embryogenesis. These data demonstrate prolonged and maintained expression by Kalooping, a technique that can be used for permanent spatiotemporal genetic fate mapping and targeted transgene expression in zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
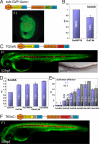
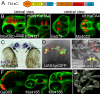
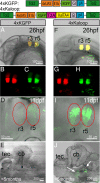

References
-
- Scheer N, Campos-Ortega JA. Use of the Gal4-UAS technique for targeted gene expression in the zebrafish. Mech Dev. 1999;80:153–158. - PubMed
-
- Deiters A, Yoder JA. Conditional transgene and gene targeting methodologies in zebrafish. Zebrafish. 2006;3:415–429. - PubMed
-
- Scott EK, et al. Targeting neural circuitry in zebrafish using GAL4 enhancer trapping. Nat Methods. 2007;4:323–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

