Effects of vitamin E on mitochondrial dysfunction and asthma features in an experimental allergic murine model
- PMID: 19628725
- PMCID: PMC2763843
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00459.2009
Effects of vitamin E on mitochondrial dysfunction and asthma features in an experimental allergic murine model
Abstract
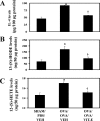
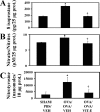
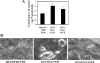
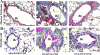
We showed recently that IL-4 causes mitochondrial dysfunction in allergic asthma. IL-4 is also known to induce 12/15-lipoxygenase (12/15-LOX), a potent candidate molecule in asthma. Because vitamin E (Vit-E) reduces IL-4 and inhibits 12/15-LOX in vitro, here we tested the hypothesis that Vit-E may be effective in restoring key mitochondrial dysfunctions, thus alleviating asthma features in an experimental allergic murine model. Ovalbumin (OVA)-sensitized and challenged male BALB/c mice showed the characteristic features of asthma such as airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), airway inflammation, and airway remodeling. In addition, these mice showed increase in the expression and metabolites of 12/15-LOX, reduction in the activity and expression of the third subunit of mitochondrial cytochrome-c oxidase, and increased cytochrome c in lung cytosol, which indicate that OVA sensitization and challenge causes mitochondrial dysfunction. Vit-E was administered orally to these mice, and 12/15-LOX expression, key mitochondrial functions, ultrastructural changes of mitochondria in bronchial epithelia, and asthmatic parameters were determined. Vit-E treatment reduced AHR, Th2 response including IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and OVA-specific IgE, eotaxin, transforming growth factor-beta1, airway inflammation, expression and metabolites of 12/15-LOX in lung cytosol, lipid peroxidation, and nitric oxide metabolites in the lung, restored the activity and expression of the third subunit of cytochrome-c oxidase in lung mitochondria and bronchial epithelia, respectively, reduced the appearance of cytochrome c in lung cytosol, and also restored mitochondrial ultrastructural changes of bronchial epithelia. In summary, these findings show that Vit-E reduces key mitochondrial dysfunctions and alleviates asthmatic features.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Esculetin restores mitochondrial dysfunction and reduces allergic asthma features in experimental murine model.J Immunol. 2009 Aug 1;183(3):2059-67. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900342. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19570833
-
Baicalein reduces airway injury in allergen and IL-13 induced airway inflammation.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 30;8(4):e62916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062916. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23646158 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine H4 receptor antagonism diminishes existing airway inflammation and dysfunction via modulation of Th2 cytokines.Respir Res. 2010 Jun 24;11(1):86. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-86. Respir Res. 2010. PMID: 20573261 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IL-13 and IL-4 in Asthma: Therapeutic Implications on Airway Remodeling in Severe Asthma.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Apr 21;68(1):44. doi: 10.1007/s12016-025-09045-2. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40257546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of interleukin-13 in asthma.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013 Oct;13(5):415-20. doi: 10.1007/s11882-013-0373-9. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013. PMID: 24026573 Review.
Cited by
-
Sorrel Extract Reduces Oxidant Production in Airway Epithelial Cells Exposed to Swine Barn Dust Extract In Vitro.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Aug 1;2019:7420468. doi: 10.1155/2019/7420468. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31481850 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria signaling pathways in allergic asthma.J Investig Med. 2022 Apr;70(4):863-882. doi: 10.1136/jim-2021-002098. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Investig Med. 2022. PMID: 35168999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of acetylsalicylic acid and vitamin E in modulating inflammatory cascades in chickens under lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation.Vet Res. 2019 Sep 18;50(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13567-019-0685-4. Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 31533824 Free PMC article.
-
Co-inhalation of roflumilast, rather than formoterol, with fluticasone more effectively improves asthma in asthmatic mice.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Mar;242(5):516-526. doi: 10.1177/1535370216685006. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28056550 Free PMC article.
-
12/15-lipoxygenase expressed in non-epithelial cells causes airway epithelial injury in asthma.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1540. doi: 10.1038/srep01540. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23528921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal A, Rengarajan S, Adler KB, Ram A, Ghosh B, Fahim M, Dickey BF. Inhibition of mucin secretion with MARCKS-related peptide improves airway obstruction in a mouse model of asthma. J Appl Physiol 102: 399–405, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bjørneboe A, Bjørneboe GE, Drevon CA. Absorption, transport and distribution of vitamin E. J Nutr 120: 233–242, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Chanez P, Bonnans C, Chavis C, Vachier I. 15-Lipoxygenase: a Janus enzyme? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 27: 655–658, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Cunningham ML. A mouse is not a rat is not a human: species differences exist. Toxicol Sci 70: 157–158, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

