RETRACTED: Identification of phosphorylated p38 as a novel DAPK-interacting partner during TNFalpha-induced apoptosis in colorectal tumor cells
- PMID: 19628771
- PMCID: PMC2716956
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080853
RETRACTED: Identification of phosphorylated p38 as a novel DAPK-interacting partner during TNFalpha-induced apoptosis in colorectal tumor cells
Retraction in
-
Retractions.Am J Pathol. 2017 Jan;187(1):225. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.09.019. Am J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27993239 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
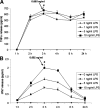
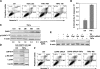
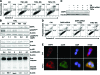
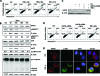
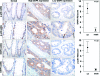
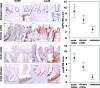
Death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) is a serine/threonine kinase that contributes to pro-apoptotic signaling on cytokine exposure. The role of DAPK in macrophage-associated tumor cell death is currently unknown. Recently, we suggested a new function for DAPK in the induction of apoptosis during the interaction between colorectal tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages. Using a cell-culture model with conditioned supernatants of differentiated/activated macrophages (U937) and human HCT116 colorectal tumor cells, we replicated DAPK-associated tumor cell death; this model likely reflects the in vivo tumor setting. In this study, we show that tumor necrosis factor-alpha exposure under conditions of macrophage activation induced DAPK-dependent apoptosis in the colorectal tumor cell line HCT116. Simultaneously, early phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (phospho-p38) was observed. We identified the phospho-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase as a novel interacting protein of DAPK in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis. The general relevance of this interaction was verified in two colorectal cell lines without functional p53 (ie, HCT116 p53(-/-) and HT29 mutant) and in human colon cancer and ulcerative colitis tissues. Supernatants of freshly isolated human macrophages were also able to induce DAPK and phospho-p38. Our findings highlight the mechanisms that underlie DAPK regulation in tumor cell death evoked by immune cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Induction of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by SB203580 requires activation of AMPK and DAPK but not p38 MAPK.Apoptosis. 2012 Apr;17(4):325-34. doi: 10.1007/s10495-011-0685-y. Apoptosis. 2012. PMID: 22170404
-
Shear stress regulates expression of death-associated protein kinase in suppressing TNFα-induced endothelial apoptosis.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Jun;227(6):2398-411. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22975. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21826654
-
DAPK plays an important role in panobinostat-induced autophagy and commits cells to apoptosis under autophagy deficient conditions.Apoptosis. 2012 Dec;17(12):1300-15. doi: 10.1007/s10495-012-0757-7. Apoptosis. 2012. PMID: 23011180
-
The DAP-kinase family of proteins: study of a novel group of calcium-regulated death-promoting kinases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Nov 4;1600(1-2):45-50. doi: 10.1016/s1570-9639(02)00443-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12445458 Review.
-
The Role of Death-Associated Protein Kinase-1 in Cell Homeostasis-Related Processes.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 16;14(6):1274. doi: 10.3390/genes14061274. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ATF2 knockdown reinforces oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in TE7 cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Aug;17(8):976-88. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12071. Epub 2013 Jun 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23800081 Free PMC article.
-
Shear stress attenuates apoptosis due to TNFα, oxidative stress, and serum depletion via death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) expression.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Mar 18;8:85. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1037-8. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 25890206 Free PMC article.
-
Updates from the Intestinal Front Line: Autophagic Weapons against Inflammation and Cancer.Cells. 2012 Aug 21;1(3):535-57. doi: 10.3390/cells1030535. Cells. 2012. PMID: 24710489 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced expression levels of the death-associated protein kinase and E-cadherin are correlated with the development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Exp Ther Med. 2013 Mar;5(3):972-976. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.916. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 23408147 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Functions of Death-Associated Protein Kinases through Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Related Signals.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 4;19(10):3031. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103031. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30287790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deiss LP, Feinstein E, Berissi H, Cohen O, Kimchi A. Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the gamma interferon-induced cell death. Genes Dev. 1995;9:15–30. - PubMed
-
- Jang CW, Chen CH, Chen CC, Chen JY, Su YH, Chen RH. TGF-beta induces apoptosis through Smad-mediated expression of DAP-kinase. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;4:51–58. - PubMed
-
- Martoriati A, Doumont G, Alcalay M, Bellefroid E, Pelicci PG, Marine JC. DAPK1, encoding an activator of a p19ARF-p53 mediated apoptotic checkpoint, is a transcription target of p53. Oncogene. 2005;24:1461–1466. - PubMed
-
- Raveh T, Droguett G, Horwitz MS, DePinho RA, Kimchi A. DAP kinase activates a p19ARF/p53-mediated apoptotic checkpoint to suppress oncogenic transformation. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

