Motile cilia of human airway epithelia are chemosensory
- PMID: 19628819
- PMCID: PMC2894709
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1173869
Motile cilia of human airway epithelia are chemosensory
Abstract
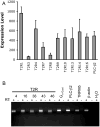
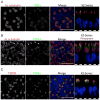
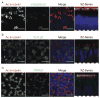
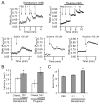
Cilia are microscopic projections that extend from eukaryotic cells. There are two general types of cilia; primary cilia serve as sensory organelles, whereas motile cilia exert mechanical force. The motile cilia emerging from human airway epithelial cells propel harmful inhaled material out of the lung. We found that these cells express sensory bitter taste receptors, which localized on motile cilia. Bitter compounds increased the intracellular calcium ion concentration and stimulated ciliary beat frequency. Thus, airway epithelia contain a cell-autonomous system in which motile cilia both sense noxious substances entering airways and initiate a defensive mechanical mechanism to eliminate the offending compound. Hence, like primary cilia, classical motile cilia also contain sensors to detect the external environment.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cell biology. Using taste to clear the air(ways).Science. 2009 Aug 28;325(5944):1081-2. doi: 10.1126/science.1179180. Science. 2009. PMID: 19713515 No abstract available.
References
-
- Singla V, Reiter JF. Science. 2006;313:629. - PubMed
-
- Marshall WF, Nonaka S. Curr Biol. 2006;16:R604. - PubMed
-
- Fliegauf M, Benzing T, Omran H. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:880. - PubMed
-
- Basu B, Brueckner M. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008;85:151. - PubMed
-
- Hirokawa N, Tanaka Y, Okada Y, Takeda S. Cell. 2006;125:33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

