Synchronous and stochastic patterns of gene activation in the Drosophila embryo
- PMID: 19628867
- PMCID: PMC4280267
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1173976
Synchronous and stochastic patterns of gene activation in the Drosophila embryo
Abstract
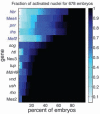
Drosophila embryogenesis is characterized by rapid transitions in gene activity, whereby crudely distributed gradients of regulatory proteins give way to precise on/off patterns of gene expression. To explore the underlying mechanisms, a partially automated, quantitative in situ hybridization method was used to visualize expression profiles of 14 developmental control genes in hundreds of embryos. These studies revealed two distinct patterns of gene activation: synchronous and stochastic. Synchronous genes display essentially uniform expression of nascent transcripts in all cells of an embryonic tissue, whereas stochastic genes display erratic patterns of de novo activation. RNA polymerase II is "pre-loaded" (stalled) in the promoter regions of synchronous genes, but not stochastic genes. Transcriptional synchrony might ensure the orderly deployment of the complex gene regulatory networks that control embryogenesis.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

