The pch2Delta mutation in baker's yeast alters meiotic crossover levels and confers a defect in crossover interference
- PMID: 19629178
- PMCID: PMC2709914
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000571
The pch2Delta mutation in baker's yeast alters meiotic crossover levels and confers a defect in crossover interference
Abstract
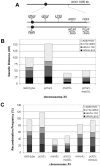
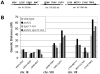
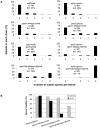
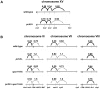
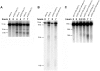
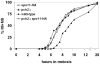
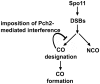
Pch2 is a widely conserved protein that is required in baker's yeast for the organization of meiotic chromosome axes into specific domains. We provide four lines of evidence suggesting that it regulates the formation and distribution of crossover events required to promote chromosome segregation at Meiosis I. First, pch2Delta mutants display wild-type crossover levels on a small (III) chromosome, but increased levels on larger (VII, VIII, XV) chromosomes. Second, pch2Delta mutants show defects in crossover interference. Third, crossovers observed in pch2Delta require both Msh4-Msh5 and Mms4-Mus81 functions. Lastly, the pch2Delta mutation decreases spore viability and disrupts crossover interference in spo11 hypomorph strains that have reduced levels of meiosis-induced double-strand breaks. Based on these and previous observations, we propose a model in which Pch2 functions at an early step in crossover control to ensure that every homolog pair receives an obligate crossover.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Comment in
-
PCH'ing together an understanding of crossover control.PLoS Genet. 2009 Jul;5(7):e1000576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000576. Epub 2009 Jul 24. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19629169 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis of baker's yeast Msh4-Msh5 reveals a threshold crossover level for meiotic viability.PLoS Genet. 2010 Aug 26;6(8):e1001083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001083. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20865162 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Crossover Frequency and Interference for Obligate Crossovers in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Meiosis.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 May 5;7(5):1511-1524. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.040071. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28315832 Free PMC article.
-
Pch2 links chromosome axis remodeling at future crossover sites and crossover distribution during yeast meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2009 Jul;5(7):e1000557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000557. Epub 2009 Jul 24. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19629172 Free PMC article.
-
Balancing the checks: surveillance of chromosomal exchange during meiosis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Aug;34(Pt 4):554-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0340554. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16856858 Review.
-
Sex and the single cell: meiosis in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10450-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10450. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7479818 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ZYP1-mediated recruitment of PCH2 to the synaptonemal complex remodels the chromosome axis leading to crossover restriction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Dec 9;50(22):12924-12937. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1160. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36504011 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting spore-autonomous fluorescent protein expression to quantify meiotic chromosome behaviors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2011 Oct;189(2):423-39. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.131326. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21840861 Free PMC article.
-
A Computational Approach to Estimating Nondisjunction Frequency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Jan 8;6(3):669-82. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.024380. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 26747203 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved ATPase PCH-2 controls the number and distribution of crossovers by antagonizing their formation in C. elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 19:2024.08.13.607819. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.13.607819. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2025 Feb 18;13:RP102409. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102409. PMID: 39185160 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Meiotic checkpoints and the interchromosomal effect on crossing over in Drosophila females.Fly (Austin). 2011 Apr-Jun;5(2):134-40. doi: 10.4161/fly.5.2.14767. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Fly (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21339705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roeder GS. Meiotic chromosomes: it takes two to tango. Genes Dev. 1997;11:2600–2621. - PubMed
-
- Buonomo SB, Clyne RK, Fuchs J, Loidl J, Uhlmann F, Nasmyth K. Disjunction of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I depends on proteolytic cleavage of the meiotic cohesin Rec8 by separin. Cell. 2000;103:387–398. - PubMed
-
- Bickel SE, Orr-Weaver TL, Balicky EM. The sister-chromatid cohesion protein ORD is required for chiasma maintenance in Drosophila oocytes. Curr Biol. 2002;12:925–929. - PubMed
-
- Hodges CA, Revenkova E, Jessberger R, Hassold TJ, Hunt PA. SMC1beta-deficient female mice provide evidence that cohesins are a missing link in age-related nondisjunction. Nat Genet. 2005;37:1351–1355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

