TLR2-dependent inhibition of macrophage responses to IFN-gamma is mediated by distinct, gene-specific mechanisms
- PMID: 19629181
- PMCID: PMC2710511
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006329
TLR2-dependent inhibition of macrophage responses to IFN-gamma is mediated by distinct, gene-specific mechanisms
Abstract
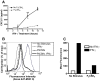
Mycobacterium tuberculosis uses multiple mechanisms to avoid elimination by the immune system. We have previously shown that M. tuberculosis can inhibit selected macrophage responses to IFN-gamma through TLR2-dependent and -independent mechanisms. To specifically address the role of TLR2 signaling in mediating this inhibition, we stimulated macrophages with the specific TLR2/1 ligand Pam(3)CSK(4) and assayed responses to IFN-gamma. Pam(3)CSK(4) stimulation prior to IFN-gamma inhibited transcription of the unrelated IFN-gamma-inducible genes, CIITA and CXCL11. Surface expression of MHC class II and secretion of CXCL11 were greatly reduced as well, indicating that the reduction in transcripts had downstream effects. Inhibition of both genes required new protein synthesis. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we found that TLR2 stimulation inhibited IFN-gamma-induced RNA polymerase II binding to the CIITA and CXCL11 promoters. Furthermore, TATA binding protein was unable to bind the TATA box of the CXCL11 promoter, suggesting that assembly of transcriptional machinery was disrupted. However, TLR2 stimulation affected chromatin modifications differently at each of the inhibited promoters. Histone H3 and H4 acetylation was reduced at the CIITA promoter but unaffected at the CXCL11 promoter. In addition, NF-kappaB signaling was required for inhibition of CXCL11 transcription, but not for inhibition of CIITA. Taken together, these results indicate that TLR2-dependent inhibition of IFN-gamma-induced gene expression is mediated by distinct, gene-specific mechanisms that disrupt binding of the transcriptional machinery to the promoters.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
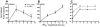
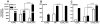



Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19-kDa lipoprotein inhibits IFN-gamma-induced chromatin remodeling of MHC2TA by TLR2 and MAPK signaling.J Immunol. 2006 Apr 1;176(7):4323-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.7.4323. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16547269
-
ESAT6 differentially inhibits IFN-γ-inducible class II transactivator isoforms in both a TLR2-dependent and -independent manner.Immunol Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;90(4):411-20. doi: 10.1038/icb.2011.54. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 21670739
-
Mycobacteria inhibition of IFN-gamma induced HLA-DR gene expression by up-regulating histone deacetylation at the promoter region in human THP-1 monocytic cells.J Immunol. 2005 May 1;174(9):5687-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.9.5687. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15843570
-
Mycobacterium avium inhibition of IFN-gamma signaling in mouse macrophages: Toll-like receptor 2 stimulation increases expression of dominant-negative STAT1 beta by mRNA stabilization.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 15;171(12):6766-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.12.6766. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14662881
-
IFN-gamma regulation of class II transactivator promoter IV in macrophages and microglia: involvement of the suppressors of cytokine signaling-1 protein.J Immunol. 2001 Feb 15;166(4):2260-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.4.2260. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11160280
Cited by
-
DGCR8 deficiency impairs macrophage growth and unleashes the interferon response to mycobacteria.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Mar 26;4(6):e202000810. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000810. Print 2021 Jun. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 33771876 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the maturation of human monocytes into immunosuppressive macrophages.Blood Adv. 2017 Dec 4;1(26):2510-2519. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017011221. eCollection 2017 Dec 12. Blood Adv. 2017. PMID: 29296902 Free PMC article.
-
B Cells Producing Type I IFN Modulate Macrophage Polarization in Tuberculosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Mar 15;197(6):801-813. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201707-1475OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29161093 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for postinitiation regulation of mRNA biogenesis in tuberculosis.J Immunol. 2013 Mar 15;190(6):2747-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202185. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23378427 Free PMC article.
-
STAT1 is a sex-specific tumor suppressor in colitis-associated colorectal cancer.Mol Oncol. 2018 Apr;12(4):514-528. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12178. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Mol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29419930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000;406:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Dunne A, O'Neill LA. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflammation and host defense. Sci STKE. 2003;2003:re3. - PubMed
-
- Foster SL, Hargreaves DC, Medzhitov R. Gene-specific control of inflammation by TLR-induced chromatin modifications. Nature. 2007;447:972–978. - PubMed
-
- Lopez M, Sly LM, Luu Y, Young D, Cooper H, et al. The 19-kDa Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein induces macrophage apoptosis through Toll-like receptor-2. J Immunol. 2003;170:2409–2416. - PubMed
-
- Mosser DM. The many faces of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;73:209–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

