Regulation of BCRP (ABCG2) and P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) by cytokines in a model of the human blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 19629677
- PMCID: PMC11498628
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-009-9431-1
Regulation of BCRP (ABCG2) and P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) by cytokines in a model of the human blood-brain barrier
Abstract
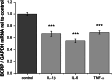
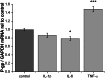
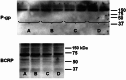
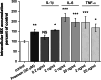
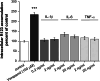
Brain capillary endothelial cells form the blood-brain barrier (BBB), a highly selective permeability membrane between the blood and the brain. Besides tight junctions that prevent small hydrophilic compounds from passive diffusion into the brain tissue, the endothelial cells express different families of drug efflux transport proteins that limit the amount of substances penetrating the brain. Two prominent efflux transporters are the breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein (P-gp). During inflammatory reactions, which can be associated with an altered BBB, pro-inflammatory cytokines are present in the systemic circulation. We, therefore, investigated the effect of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) on the expression and activity of BCRP and P-gp in the human hCMEC/D3 cell line. BCRP mRNA levels were significantly reduced by IL-1beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha. The strongest BCRP suppression at the protein level was observed after IL-1beta treatment. IL-1beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha also significantly reduced the BCRP activity as assessed by mitoxantrone uptake experiments. P-gp mRNA levels were slightly reduced by IL-6, but significantly increased after TNF-alpha treatment. TNF-alpha also increased protein expression of P-gp but the uptake of the P-gp substrate rhodamine 123 was not affected by any of the cytokines. This in vitro study indicates that expression levels and activity of BCRP, and P-gp at the BBB may be altered by acute inflammation, possibly affecting the penetration of their substrates into the brain.
Figures
References
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AM, Miller DS (2007) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and endothelin-1 increase P-glycoprotein expression and transport activity at the blood–brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol 71:667–675 - PubMed
-
- Breedveld P, Pluim D, Cipriani G, Wielinga P, van Tellingen O, Schinkel AH, Schellens JH (2005) The effect of Bcrp1 (Abcg2) on the in vivo pharmacokinetics and brain penetration of imatinib mesylate (Gleevec): implications for the use of breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein inhibitors to enable the brain penetration of imatinib in patients. Cancer Res 65:2577–2582 - PubMed
-
- Cisternino S, Mercier C, Bourasset F, Roux F, Scherrmann JM (2004) Expression, up-regulation, and transport activity of the multidrug-resistance protein Abcg2 at the mouse blood–brain barrier. Cancer Res 64:3296–3301 - PubMed
-
- Cooray HC, Blackmore CG, Maskell L, Barrand MA (2002) Localisation of breast cancer resistance protein in microvessel endothelium of human brain. NeuroReport 13:2059–2063 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

