Gene expression pattern and downregulation of DNA methyltransferase 1 using siRNA in porcine somatic cells
- PMID: 19630269
- PMCID: PMC6042044
- DOI: 10.3727/105221609788681222
Gene expression pattern and downregulation of DNA methyltransferase 1 using siRNA in porcine somatic cells
Abstract
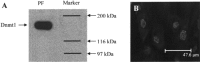
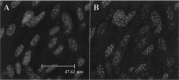
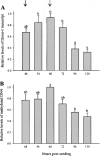
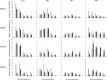
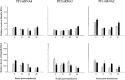
DNA methylation plays a significant role in the expression of the genetic code and affects early growth and development through their influence on gene expression. Manipulation of the DNA methylation marks of differentiated cells will allow a better understanding of the different molecular processes associated with chromatin structure and gene expression. The objective of this study was to identify small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) with the ability to reduce DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) mRNA and consequently decrease Dnmt1 protein as well as DNA methylation in porcine cells. Fibroblasts from four porcine fetuses were established and cultured in 5% CO2 in air at 38 degrees C. Optimal transfection conditions were evaluated using a FITC-labeled control siRNA. Four Dnmt1-specific siRNAs were evaluated upon transfection of each cell line. A nonsilencing siRNA was used as a negative control. The expression patterns of Dnmt1 were analyzed by Q-PCR. The combination of 1 microg of siRNA and a 1:6 siRNA to transfection reagent ratio produced the highest transient transfection rates without affecting cell viability. Downregulation of Dnmt1 varied between siRNAs. Transfection of porcine cells with highly effective siRNAs resulted in a drastic reduction of Dnmt1 mRNA and a slight decrease in protein production. However, this small reduction in the protein concentration induced significant genomic hypomethylation. These data suggest that although Dnmt1 mRNA abundance plays an important role during protein regulation, Dnmt1 enzyme is mainly posttranscriptionally regulated. Subsequent use of these cells for cloning, differentiation, and cancer studies will provide insight as to how methylation of the DNA affects genomic reprogramming.
Figures
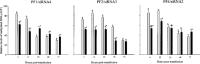
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase 1 expression in bovine fibroblast cells used for nuclear transfer.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2009;21(6):785-95. doi: 10.1071/RD08233. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2009. PMID: 19567221
-
DNA methylation and not H3K4 trimethylation dictates the expression status of miR-152 gene which inhibits migration of breast cancer cells via DNMT1/CDH1 loop.Exp Cell Res. 2016 Aug 15;346(2):176-87. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.07.023. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Exp Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 27475839
-
Expression of DNMT1 and DNMT3a are regulated by GLI1 in human pancreatic cancer.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027684. Epub 2011 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2011. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Nov 9;18(11):e0294385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294385. PMID: 22110720 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Towards a pharmacology of DNA methylation.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Jul;22(7):350-4. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)01713-2. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001. PMID: 11431029 Review.
-
Mammalian cytosine DNA methyltransferase Dnmt1: enzymatic mechanism, novel mechanism-based inhibitors, and RNA-directed DNA methylation.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(1):92-106. doi: 10.2174/092986708783330700. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18220765 Review.
Cited by
-
Dnmt1s in donor cells is a barrier to SCNT-mediated DNA methylation reprogramming in pigs.Oncotarget. 2017 May 23;8(21):34980-34991. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16507. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28380421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams A. M.; Pratt S. L.; Stice S. L. Knockdown of the Dnmt1s transcript using small interfering RNA in primary murine and bovine fibroblast cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 72:311–319; 2005. - PubMed
-
- Bestor T. H. The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9:2395–2402; 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bridge A. J.; Pebernard S.; Ducraux A.; Nicoulaz A. L.; Iggo R. Induction of an interferon response by RNAi vectors in mammalian cells. Nat. Genet. 34:263–264; 2003. - PubMed
-
- Cezar G. G. Epigenetic reprogramming of cloned animals. Cloning Stem Cells 5:165–180; 2003. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
