The many faces of tissue factor
- PMID: 19630786
- PMCID: PMC2834482
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03368.x
The many faces of tissue factor
Abstract
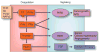
Tissue factor (TF) is a member of the cytokine receptor superfamily and binds FVII/VIIa. The TF:FVIIa complex has both procoagulant and signaling activities. It functions in many biological processes, including hemostasis, thrombosis, inflammation, angiogenesis and tumor growth. Importantly, TF is essential for hemostasis. However, increased TF expression within atherosclerotic plaques and elevated levels of circulating TF-positive micro particles promote thrombosis. TF increases inflammation by enhancing intravascular fibrin deposition, by increasing the formation of pro-inflammatory fragments of fibrin and by generating coagulation proteases, including FVIIa, FXa and thrombin, that activate protease-activated receptors (PARs). In endotoxemia and sepsis, TF-dependent thrombin generation and activation of PAR1 on dendritic cells enhance inflammation. Finally, the TF:FVIIa complex contributes to tumor growth by activating PAR2.
Conflict of interest statement
N. M. is a consultant for Daiichi Sankyo, Inc and is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Othera Pharmaceuticals, Thrombotargets and King Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffman M, Colina CM, McDonald AG, Arepally G, Pedersen L, Monroe DM. Tissue factor around dermal vessels has been bound factor VII in the absence of injury. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:1403–8. - PubMed
-
- Mackman N. Tissue-specific hemostasis in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:2273–81. - PubMed
-
- Mackman N. Tissue-specific hemostasis: role of tissue factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:303–5. - PubMed
-
- Mackman N, Tilley RE, Key NS. Role of the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation in hemostasis and thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:1687–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

