Causal supports for early word learning
- PMID: 19630905
- PMCID: PMC2786819
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2009.01328.x
Causal supports for early word learning
Abstract
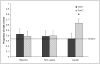
What factors determine whether a young child will learn a new word? Although there are surely numerous contributors, the current investigation highlights the role of causal information. Three-year-old children (N = 36) were taught 6 new words for unfamiliar objects or animals. Items were described in terms of their causal or noncausal properties. When tested only minutes after training, no significant differences between the conditions were evident. However, when tested several days after training, children performed better on words trained in the causal condition. These results demonstrate that the well-documented effect of causal information on learning and categorization extends to word learning in young children.
Figures
References
-
- Ahn W-k. Why are different features central for natural kinds and artifacts? The role of causal status in determining feature centrality. Cognition. 1998;69:135–178. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JR. The architecture of cognition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1983.
-
- Balaban MT, Waxman SR. Do words facilitate object categorization in 9-month-old infants? Journal of Experimental Child Psychology. 1997;64:3–26. - PubMed
-
- Barr R, Hayne H. The effect of event structure on imitation in infancy: Practice makes perfect? Infant Behavior & Development. 1996;19:253–257.
-
- Barrett SE, Abdi H, Murphy GL, Gallagher JM. Theory-based correlations and their role in children’s concepts. Child Development. 1993;64:1595–1616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

